Difference between revisions of "Functional Testing"
(→Software Test Tracker Creation - NEW) |
(→Software Test Tracker Creation - NEW) |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
The flow is showed in the following figure: | The flow is showed in the following figure: | ||
| − | [[File:SWTestWorkflow.png|center]] | + | [[File:SWTestWorkflow.png| center]] |
Revision as of 14:34, 20 February 2017
Go to Test_Plan section.
Contents
Introduction
The objective of the Functional Testing activity in gCube is to ensure that all the components gCube services and public interfaces:
- are conform to their specification
- are free from erroneous or malfunction
- can be run in the defined system requirement
- are free from code anomalies and coding errors
The goal of functional testing is to assure the appropriate quality of the gCube software. Testing, in general, is not a procedure to find bugs, but to check that the software works in accordance with the specification, architectural and detailed design documents. In addition, the testing activity has to ensure that the software is easy to use and gives appropriate response in the case of wrong usage or defects that cannot entirely be eliminated. Testing is planned according to these goals.
The gCube software is composed by three types of components: services, libraries, and portlets. While deployment of services and libraries are tested with the Deployment tests, the functionality of portlets is tested through a specific procedure. Since portlets rely on services and libraries to perform their functions, testing the portlets functionalities implicitly tests also the functionalities of services and libraries.
Portlet Functional Testing - UPDATED
The Portlets composing gCube have been required to pass a functional testing procedure in order to be made available for end users. The actors involved in the procedure are: the portal manager, the infrastructure manager, and the owner (generally , portlet application domain experts or the developer of the Portlet or the responsible of the application) . The owners (portlet application domain experts) are expert users of a specific application. The owner (domain expert) knows very well all the possible interactions between the end user and the user interface. In some specific cases, they could be application developers or application owners.
The procedure starts by analysing the software artefacts included in the release along with their software dependencies. This task is carried out manually by the portal manager. Each portlet artefact which is released must be part of the functional testing procedure. Also, if anything in the dependency chain of a Portlet X is released, then X has to be functionally tested too.
The Portlets Functional Testing procedure consists of 4 stages:
- Web Archive check: every Portlet web archive released is verified to contain all the necessary files needed for its correct deployment. If the check is not passed the Portlet developer is notified through a new ticket of type integration issue;
- Back-end Service check: The portal manager and the infrastructure manager make sure that the back-end services of the Portlet application are ready and fully functional in the testing / pre-production infrastructure.
- Rendering check: every Portlet web archive passing stage no. 1 is then actually deployed into the pre-production portal to check if it renders correctly. In this stage there are few things that could make the Portlet not render correctly. For instance, the GWT compilation could fail during Web Archive creation, or the developer could have used some CSS classes that clash with those of the iMarine Gateway. If the check is not passed the Portlet developer is notified through a new ticket of type integration issue;
- Functional Test: When stage 1 and 2 and 3 are completed the functional test is assigned to the testing team which performs it by following the Software Testing Plan. An updating of the Functional test procedure is discussed to use the the Redmine tool to track the functional testing activities and dismiss the Functional Master Table. The new Software Test procedure is provided in the Functional Test (FT) Procedure section.
Software Testing Plan
The Software Testing Plan #1413 is created in the VRE Folders > gCube > Portlet Testing Plans containing two folders: Material and Releases.
The Material directory provides the following information:
- the general XLS template to be instantiated by each portlet developer for compiling the Testing Plan and
- the portlet folder (created by Portal Manager) for each portlet to be functionality tested. The syntax used to create the portlet folder
will be: $portlet_name_folder. Every developer will create the actual testing plan into Material/$portlet_name_folder including by adding additional files required for the test (e.g. cvs_files). To describe the functional tests, the developer will use the Portlet Testing Plan Template; this file will be pasted and completed into the Release folders by the testers.
A Task (Redmine Ticket) will be assigned, by the Release Manager, to each portlet developer.
The Releases directory contains a folder for each gCube release containing the tests to be executed.
The Portal Manager creates (in this directory) the gCube release directory and the portlets directories related.
Functional Test (FT) Procedure - UPDATED
A new procedure is released using the Redmine tool to track the testing activities. In this phase the principal role involved are : Tester Manager.
The action for the TestManager are:
- to create the new Release Software Test Ticket (master ticket and its sub-tickets);
- to create the query;
- to clone the master ticket acting as template for the portlet testing.
The master ticket and its sub-tickets can be used as template with Progress filed at "0" and Status field at "New" to create the other tickets. For the testing of each release the TMAN copies from that template. In this way, only the sprint is changed (in one action thanks to the multi-selection).
The fields (for every tickets) to fill are:
- Project : gCube
- Tracker : SW Test;
- Subject : name of the portlets (plus version) to test or name of the Master Ticket.
- org.gcube.subsystemName.componentName.version (SW Test) for the component test ticket. For example: org.gcube.application.aquamaps.aquamapsspeciesview.1-3-4 (SW Test).
- gCube SW Test Release x.x.x for the Master ticket. For example gCube SW Test Release 4.3.0.
- Priority : Normal;
- Assignee: Tester, Developer, Infrastrucute or Portal Manager, Release. This assignment depend on the action to do (test, deploy, solve the issue and so on);
- Category : name of the subsystem portlet (e.g. portlets-admin);
- Sprint : Release x.x.x - FT Testing. For example: Release 4.3.0 - FT Testing;
- Parent Task: Master SW Test Ticket (only for the software test components ticket). The parent task for the Master Ticket is the Project Task ticket;
- Start Date: The date of the ticket creation;
- End date: Date of the deadline ;
- Progress: updated when the testing activities is in progress (included not only test but the solution of the issue). Only the first time the progress is 0.
Before to start with the functional test portlets some action were occured:
- The Release Manager asked to every partners to suggest the persons that forms the testing team. A table of the role and assignment is created: Role_Tester.
- Some recommendations were considered mandatory as:
- For every release a Software Test Tracker is created.
Software Test Tracker Creation - NEW
The flow for the Tracker Releases is:
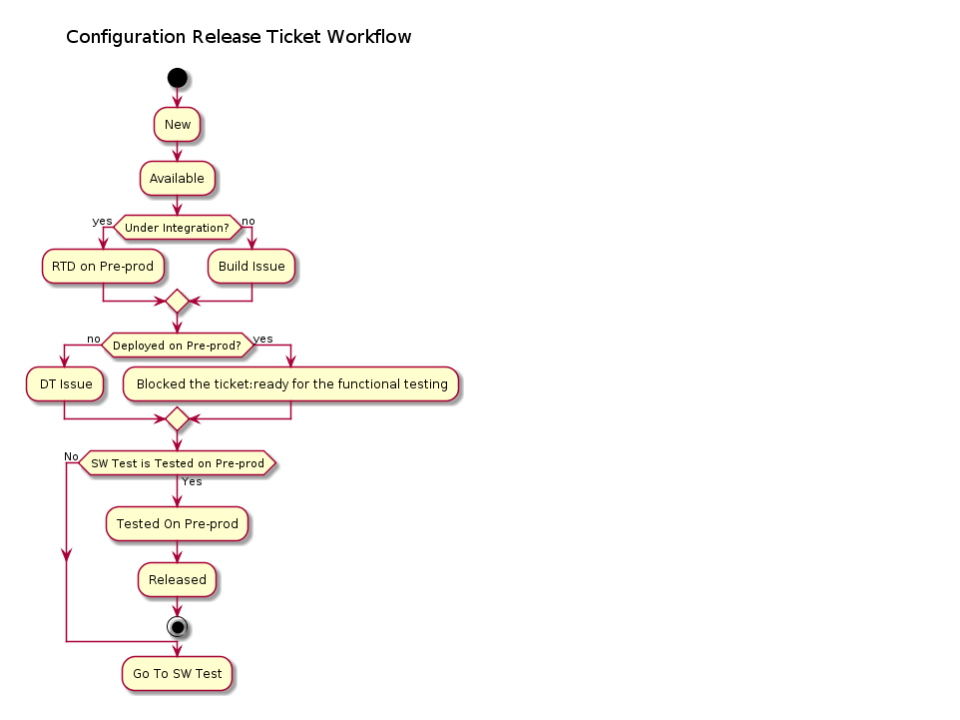
New > Available > Under Integration > Build Issue (it goes back to under integration) OR RTD on Preprod > Deployed on Preprod or DT Issue (it goes back to Deployed On Preprod) > Released The flow is showed in the following figure:
The flow for the Software Test Tracker is:
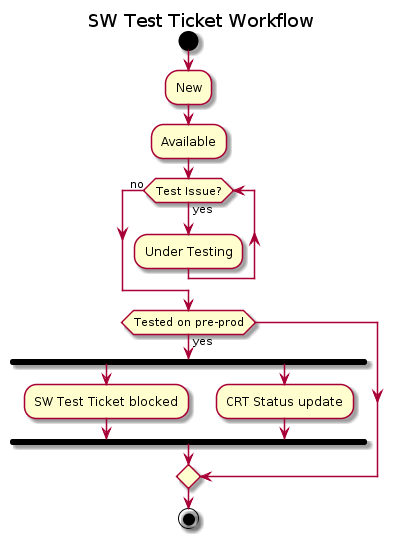
New > Available (we verify that the back-end service is up&running, if so move to next status) > Under testing (The tester tests the app) > FT Issue (it goes back Available) OR Tested on preprod.
The flow is showed in the following figure:
- The Master Ticket is created by the Release or Portal Manager.
- The SW Test Portlet Tickets will be created copying the Master Ticket (it's considered the template of the SW Test Portlet).
- The SW Test Portlet are available after the services are deployed on pre-production and after the Deployer Manager following the procedure as reported in the (Releases Integration).
The Release Manager or the Portal Manager block the Tracker Releases and update the SW Test Tracker from Available to Under Testing.
- The Tester can start with the functional test when Deployer/Infrastructure Manager updates the CRT : {status: Under Integration -> Deployed on Preprod}. The following steps are executed:
- The Tester copies the TestPlan, with the results of the test, in the Releases directory.
For example: the tester tests the invites-friends.1-1-0 portlets. The Tester copies the TestPlan for this portlets into Releases/org.gcube.4.0.0/invites-friends.1-1-0.
- The Tester updated the TestPlan , provided in the Releases directory, with the results for the functional testing.
For example, in the case of the invites-friends, the Tester updates the TestPlan with the functional testing results for this component.
In case the functional testing failed , the Tester opens the issue in the following way:
1) The Tester updates the CRT:{status: Deployed on Preprod -> FT Issue, comment: <issue description>}.
The comment should always include a link to a relevant log/report file. The Tester updates the TestPlan provided the number of the issue ticket too (field "Link to the Issue" ) and describing the test results (fied "Results"), too.
2) After the resolution of the issue, the developer updates the CRT:{status: FT Issue -> Under Itegration, comment: <issue description>}.Now. the Infrastructure Manager can be re-deployed the service and updates the CRT status : {status: Under Integration -> Deployed on Preprod, comment: <issue description>}. The tester knows that can repeat the testing and if the test passed, updates the CRT:{status: Deployed On Preprod -> Tested on Preprod, comment: <issue description>}. Otherwise he/she repeats the step 1) (the status return in FT Issue). The Test updates the TestPlan with the new test results (field "Results"), too.
NOTE: - Test issue = The test is fails. - Tested on Preprod : indicated that the developer and/or the portal manager or the preprod infrastructure manager are confident that the component behave as expected and can be released as is.
The pre-production infrastructure is provided for the functional testing hosted at CNR.
Roles
The functionality testing activity foresees the involvement of the following roles:
- Tester
- Developer
Tester - UPDATED
The details about the role of the testers are hosted on the Testers wiki page.
The Tester is responsible:
- for the execution of the functionality tests and to submit functionality test bugs
- to fill the dedicated Portlet Testing Plan Template and the creation of the SW Test ticket.
- to track the FT Issue through the use of the track system issue tool (ref. D4Science support).
The tester starts with the functional test when Deployer/Infrastructure Manager updates the CRT status: {status: Under Integration -> Deployed on Preprod}.
In case the functional testing fails , the Tester opens the issue updating the SW Test Tracker: {status: Under Testing -> Test Issue, comment: <issue description>}.
The comment should always include a link to a relevant log/report file.
After the resolution of the issue, the developer updates the SW Test Tracker {status: Test Issue -> Under Testing, comment: <issue description>}. The Infrastructure Manager know that the portlets must be re-deployed (and after the deploy on Preprod the Tester can repeat the test).
The Tester repeats the testing and, if the test not fails, updates the SW Test Tracker: {status: Under Testing -> Tested on Preprod, comment: <issue description>}.
Otherwise, a new issue is opened and the track status returns in Test Issue.
Developer - UPDATED
The details about the role of the developers are hosted on Developers wiki page. The developer is:
- responsible for fixing (functionality and no) test bugs
- carried out by JRA members
- responsible to fill the dedicated Portlet Testing Plan Template as described in the previous section.
Infrastructure
The execution of functionality tests requires a gCube testing infrastructure fully functional. A detailed description of the testing infrastructure can be found Testing Infrastructure