Difference between revisions of "Integration of Maven Components"
(→Glossary) |
(→gCube Maven Reposiotries) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
= gCube Maven Reposiotries = | = gCube Maven Reposiotries = | ||
| − | * gCube Snapshots | + | '''gCube Releases''' |
| − | * gCube | + | * Contains artifacts officially released. |
| − | * gCube Externals | + | * URL: http://maven.research-infrastructures.eu/nexus/content/repositories/gcube-releases/ |
| + | * access: only release manager | ||
| + | * only release version, no re-deploy | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''gCube Snapshots''' | ||
| + | * Contains snapshot versions of of gCube components. It is used mainly during the development phase to make public and available for integration not yet released software | ||
| + | * URL: http://maven.research-infrastructures.eu/nexus/content/repositories/gcube-snapshots/ | ||
| + | * access: release manager, developers | ||
| + | * only snapshot versions, redeploy allowed | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''gCube Externals''' | ||
| + | * Contains patched versions of third party components. Those components cannot be considered part of gCube system | ||
| + | * URL: http://maven.research-infrastructures.eu/nexus/content/repositories/gcube-externals/ | ||
| + | * access: release manager | ||
= Overall strategy = | = Overall strategy = | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 5 April 2012
Contents
Introduction
This guide is meant to provide gCube's Developers with all information needed to properly configure a Maven-based gCube component in ETICS to succesfully integrate with other components in the system.
Glossary
- Maven component: a gCube component which uses Maven ad building tool
- Legacy component: a gCube component (most probably developed before iMarine project) which uses the classical building system based on ant
- Mavenizer: a tool developed within gCube project able to create a pom.xml file
Checklist for Developers
For legacy components configurations:
- be sure mavenize is called in postpublish target
- be sure that the artifact generated by the component (usually .jar, .gar, .war) is properly copied in ${prefix}
For Maven components configurations:
- be sure your component has a dependency on maven-builder
- since also gCore depends on maven-builder, if your component depends on gCore, no action is required
- if your Maven component has a parent (usually maven-parent) be sure you have a dependency in your component towards the needed parent's version
gCube Maven Reposiotries
gCube Releases
- Contains artifacts officially released.
- URL: http://maven.research-infrastructures.eu/nexus/content/repositories/gcube-releases/
- access: only release manager
- only release version, no re-deploy
gCube Snapshots
- Contains snapshot versions of of gCube components. It is used mainly during the development phase to make public and available for integration not yet released software
- URL: http://maven.research-infrastructures.eu/nexus/content/repositories/gcube-snapshots/
- access: release manager, developers
- only snapshot versions, redeploy allowed
gCube Externals
- Contains patched versions of third party components. Those components cannot be considered part of gCube system
- URL: http://maven.research-infrastructures.eu/nexus/content/repositories/gcube-externals/
- access: release manager
Overall strategy
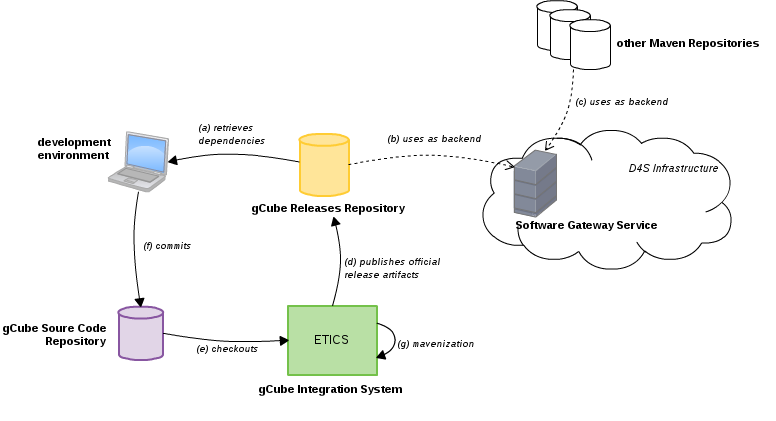
Figure below catches the main components, and their interactions, that are involved in the gCube' software integration, release and distribution.
The central element of the gCube release and distribution strategy is the gCube Releases Repository. It is a classical Maven repository where all released versions of all gCube components are stored.The gCube Releases Repository is the main distribution site for gCube Software:
- Developers configure their development machine to use gCube Releases to resolve and fetch dependencies (a) for gCube components their are developing.
- the Software Gateway service uses gCube Releases as back-end (among, potentially, other third party Maven repositories (c) ) making software stored there available for dynamic deployment within the D4Science Infrastructure.
Another central role is played by ETICS: the integration system used by gCube. It is responsible for the publication (d) in gCube Releases of artifacts that comes out from the integration of gCube components. In particular, actions performed by ETICS are:
- checkout (e), compilation and testing of gCube Maven components from the gCube' source code repository
- validation and certification of artifacts. This ensure that components published in gCube Releases satisfy the quality level defined in the gCube project
- mavenization of legacy components. This make also gCube components that builds with ant available for dependency resolution in Maven
- publication of artifacts in gCube Releases
Bringing Maven in ETICS: the maven-builder
ETICS builds take place on a remote machine on a "empty" environment. In order to properly build Maven components it is needed Maven to be installed and configured on the remote machine. All those tasks are performed by an ETICS component created for this purpose called maven-builder.
Briefly, this is what maven-builder provides:
- has a dependency on the external component maven to download and install Maven tool on the building machine
- provides the customized maven' settings file gcube-default-settings.xml which contains credentials to access gCube Snapshot repository
- overrides the default Maven's local repository location (which is not writable by ETICS)
- defines env variables for gCube repositories
- replaces original mvn command with the Maven Proxy in the PATH
- provides mavenizer script and put it in the PATH
In detail, maven-builder exports following environment variables:
MAVEN_GCUBE_RELEASES: http://maven.research-infrastructures.eu/nexus/content/repositories/gcube-releases/
MAVEN_GCUBE_SNAPSHOTS: http://maven.research-infrastructures.eu/nexus/content/repositories/gcube-snapshots/
MAVEN_LOCAL_REPOSITORY: ${moduleDir}/localrepository
MAVEN_SETTINGS: ${moduleDir}/etc/gcube-default-settings.xml
PATH: ${moduleDir}/bin:$PATH
maven-builder is a pre-requisite to build any gCube Maven component in ETICS. All maven-based components must have a direct or indirect dependency on maven-builder.
Note that also gCore depends on maven-builder. It means that, if a component depends on gCore it is not required to put the dependency on maven-builder.
Maven Proxy
Actions:
- set settings.xml file and path for maven local repository
- check that pom and ETICS versions are coherent
- run versions plugin replacing dependencies' versions forcing usage of ones stored in the local repository
- set -Dmaven.deploy.skip properly
Mavenizer
Mavenizer is a tool created with the intent of making gCube legacy components compatible with new maven components. It is able to generate a pom.xml on-the-fly from information available on component's profile.xml and ETICS configuration and upload artifacts on gCube repositories. It is meant to be used by ETICS during its builds to mavenize legacy components with a twofold benefit:
- being able to have those components in gCube Maven Repositories
- make legacy components available for Maven components in the local Maven repository for compile-time dependency resolution purposes
The snippet below shows the input parameters accepted by mavenize script.
[gabriele@gabriele-work maven-builder]$ bin/mavenize --help USAGE: bin/mavenize [flags] flags: -g,--groupId: the groupId to use in the mvn commandline (default: 'org.gcube') -k,--packaging: the type of the artifact. Default is 'jar'. (default: 'jar') -n,--artifactId: the artifactId to use in the mvn commandline. If not specified, it will be the etics module's name (default: '') -v,--version: the version to use in the mvn commandline. If not specified, it will be the etics module version (default: '') -f,--file: artifact file to mavenize. If not specified, a search will be done in the etics module home trying to find a suitable artifact (default: '') -d,--[no]forcedeploy: force deployment of artifact on remote repository (default: false) -s,--[no]dryrun: no act. Perform just a simulation (default: false) -l,--loglevel: log level. Accepted values are 0, 1, 2 (default: 1) -h,--[no]help: show this help (default: false)
All parameters are optional; if a parameter is not provided, the mavenizer tries to guess the value searching the information in component's profile.xml and/or ETICS configuration (depending on the type fo parameter).
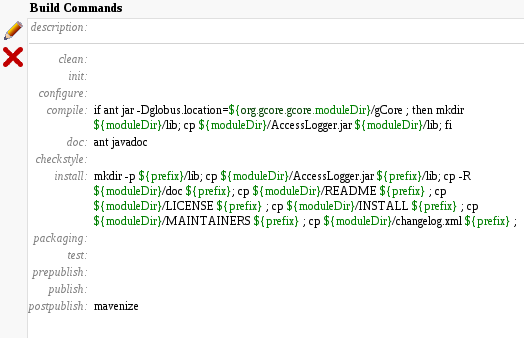
To trigger execution of mavenizer on a given legacy component, it is enough - in most of cases - to have an invocation to mavenize in the component's ETICS build configuration in target postpublish (as shown in figure below).
Note: call to mavenize should be already present in all legacy components since it has been added automatically by ETICS administrators.