Difference between revisions of "GCore Based Information System Specification"
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) (→Architecture) |
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) (→Architecture) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
[[Image:InformationSystem-Architecture.png|frame|center|Information System Architecture]] | [[Image:InformationSystem-Architecture.png|frame|center|Information System Architecture]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | They globally deliver the following functionalities with respect to the information handled: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * production and publication | ||
| + | * collection, indexing and storage | ||
| + | * discovery and consumption | ||
| + | |||
| + | The components belonging the production and publication phase are: | ||
| + | *'''IS-Registry''': this service exposes an API for publishing/un-publishing profiles of resources compliant with the Resource Model of both [[Reference_Model|first]] and [[Resource_Model_(2nd_generation)|second]] generation; | ||
| + | *'''IS-Notifier''': this service builds on top to WS-Notification to deliver notifications about changes occurring in the resources registered in the IS-Registry; it also supports other services in subscribing/unsubscribing to topics produced by the various Services; this service decouples the actual producer of the topic from the actual consumer allowing for producers re-location | ||
| + | *'''IS-gLiteBridge''': this service publishes and unpublishes resources gathered from a gLite based infrastructure that gCube services may access to | ||
| + | *'''IS-Publisher''': a library available to gCube services for publishing/un-publishing information in the IS | ||
| + | |||
| + | The component supporting the collection, indexing and storage phase is: | ||
*'''IS-InformationCollector''': a service that collects and makes available information related to the actual state of the gCube infrastructure and/or of an assigned subset of it; it exposes APIs compliant with WS-DAIX for feeding and then accessing indexed resources | *'''IS-InformationCollector''': a service that collects and makes available information related to the actual state of the gCube infrastructure and/or of an assigned subset of it; it exposes APIs compliant with WS-DAIX for feeding and then accessing indexed resources | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The components supporting the discovery and consumption phase are: | |
| − | *'''IS- | + | *'''IS-Client''': a library available to gCube services for discovering information published in the IS |
| − | + | *'''IS-Notification''': a library available to gCube services with publication/subscription/notification mechanism for Topics produced and consumed by any actor of the infrastructure compliant with WS-Notification | |
| − | *'''IS- | + | |
| − | + | ||
== Deployment == | == Deployment == | ||
Revision as of 05:02, 1 March 2012
Overview
The Information System (IS) is the core subsystem connecting producers and consumers of resources. It acts as a registry of the infrastructure by offering global and partial views of its resources and their current status and notification instruments.
The approach provided by the IS is of great support for the dynamic deployment capabilities and the interoperability solutions offered by the Resource Management facilities.
Key features
- Resource Publication, Access and Discovery
- IS is the connecting point among the resources of the e-Infrastructure
- Consistency with the new Resource Model
- IS grants publication and access to resources compliant with the Resource Model (2nd generation)
- Production level QoS - Responsiveness
- each query served in milliseconds, thousands of queries served each hour
- Production level QoS - Scalability
- infrastructures with more than 10K of resources successfully powered
- Production level QoS - Reliableness
- IS instances have been continuously up for more than one year without human intervention
- Support to Standards - WS-DAIX Specification v1.0
- full implementation of WS-DAIX v.1.0, a widely accepted standard defining a set of data access interfaces for XML data resources
- Support to Standards - XQuery 1.0
- Resource discovery can be performed through expressions compliant with XQuery 1.0
- Support to Standards - WS-Notifications
- Consumers of resources can subscribe to the IS for receiving WS-Notifications about any change occurred in they resources the are interested in
- Flexible deployment scenarios
- IS components can be deployed in several ways, to best fit the needs of an infrastructure or a specific VO
Design
Philosophy
The IS has been designed and implemented to:
- rely on standards
- support distribution at maximum and replication wherever it is possible
- abstract clients from the deployment scenario
A central role of the Information System is also to publicly manifest resources and connect them to their consumers. A consistent Resource Model has been created at the beginning of the gCube development and served for many years as a solid basis of gCube core-facilities. With the increasing openness of the system, a second generation of the model has been shaped and being integrated in the IS.
Architecture
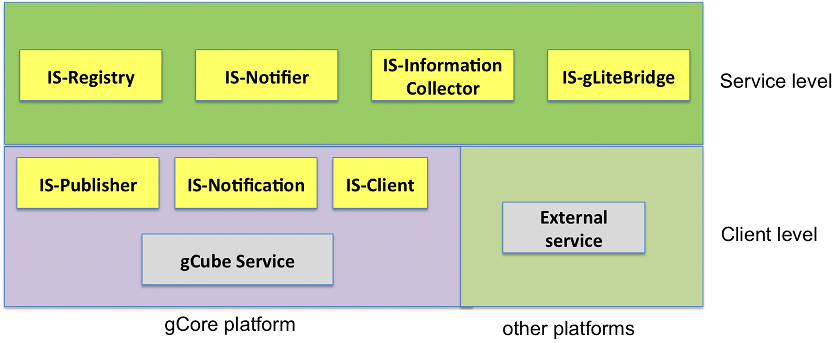
To deliver the quality of service and performances and to handle growing amounts of information (scalability), the Information System is composed by a set of Web Services and client libraries.
They globally deliver the following functionalities with respect to the information handled:
- production and publication
- collection, indexing and storage
- discovery and consumption
The components belonging the production and publication phase are:
- IS-Registry: this service exposes an API for publishing/un-publishing profiles of resources compliant with the Resource Model of both first and second generation;
- IS-Notifier: this service builds on top to WS-Notification to deliver notifications about changes occurring in the resources registered in the IS-Registry; it also supports other services in subscribing/unsubscribing to topics produced by the various Services; this service decouples the actual producer of the topic from the actual consumer allowing for producers re-location
- IS-gLiteBridge: this service publishes and unpublishes resources gathered from a gLite based infrastructure that gCube services may access to
- IS-Publisher: a library available to gCube services for publishing/un-publishing information in the IS
The component supporting the collection, indexing and storage phase is:
- IS-InformationCollector: a service that collects and makes available information related to the actual state of the gCube infrastructure and/or of an assigned subset of it; it exposes APIs compliant with WS-DAIX for feeding and then accessing indexed resources
The components supporting the discovery and consumption phase are:
- IS-Client: a library available to gCube services for discovering information published in the IS
- IS-Notification: a library available to gCube services with publication/subscription/notification mechanism for Topics produced and consumed by any actor of the infrastructure compliant with WS-Notification
Deployment
Usually, a subsystem consists of a number of number of components. This section describes the setting governing components deployment, e.g. the hardware components where software components are expected to be deployed. In particular, two deployment scenarios should be discussed, i.e. Large deployment and Small deployment if appropriate. If it not appropriate, one deployment diagram has to be produced.
Large deployment
A deployment diagram suggesting the deployment schema that maximizes scalability should be described here.
Small deployment
A deployment diagram suggesting the "minimal" deployment schema should be described here.
Use Cases
The subsystem has been conceived to support a number of use cases moreover it will be used to serve a number of scenarios. This area will collect these "success stories".
Well suited Use Cases
Less well suited Use Cases
Describe here scenarios where the subsystem partially satisfied the expectations.