Difference between revisions of "FHNManager"
(→Deployment) |
(→Functional requirements) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
* the gCube system intelligently adapt the number of SmartExecutor nodes to the actual demand. In the VRE administration portal, the VRE Manager decides the minimum and maximum number of SmartExecutor expected for the VRE. Then, the gCube system via the integration facility here described, automatically scales-in/out the pool of SmartExecutors (by creating/destroying nodes) predicting the demand for SmartExecutors by analysing VRE accounting and monitoring data. | * the gCube system intelligently adapt the number of SmartExecutor nodes to the actual demand. In the VRE administration portal, the VRE Manager decides the minimum and maximum number of SmartExecutor expected for the VRE. Then, the gCube system via the integration facility here described, automatically scales-in/out the pool of SmartExecutors (by creating/destroying nodes) predicting the demand for SmartExecutors by analysing VRE accounting and monitoring data. | ||
| − | = | + | = Requirements = |
It is possible to recognize the following functionalities that should be available in the integration facilities: | It is possible to recognize the following functionalities that should be available in the integration facilities: | ||
| + | == Functional requirements == | ||
* Registration and management of cloud providers, access credentials and cloud resources templates on a per-VRE basis. Credentials must be securely stored in the infrastructure; | * Registration and management of cloud providers, access credentials and cloud resources templates on a per-VRE basis. Credentials must be securely stored in the infrastructure; | ||
* Cloud resource lifecycle management. Creation, configuration and decommissioning of cloud resources must be supported. The integration facility allows to use templates for the configuration of cloud resources (e.g. SmartExecutor Template, cpu and memory characteristics); | * Cloud resource lifecycle management. Creation, configuration and decommissioning of cloud resources must be supported. The integration facility allows to use templates for the configuration of cloud resources (e.g. SmartExecutor Template, cpu and memory characteristics); | ||
* Accountability and monitorability. Accounting and monitoring data on usage and workload of resources created on the cloud must be collected and made available in the infrastructure. This is both a requisite to comply with D4Science infrastructure policies and for the automatic scale-in/out; | * Accountability and monitorability. Accounting and monitoring data on usage and workload of resources created on the cloud must be collected and made available in the infrastructure. This is both a requisite to comply with D4Science infrastructure policies and for the automatic scale-in/out; | ||
* User interface. The user interface is integrated in the VRE administration portal since it already contains all the other VRE administration tools | * User interface. The user interface is integrated in the VRE administration portal since it already contains all the other VRE administration tools | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Non-Functional requirements == | ||
| + | The solution should have modular architecture in order to support the integration of new cloud providers in a simple and pluggable way. | ||
= Non-Functional requiriments = | = Non-Functional requiriments = | ||
Revision as of 13:13, 4 May 2016
The integration of the gCube system with FedCloud and, in general, with research/commercial cloud providers, aims to add elasticity to the D4Science infrastructure by allowing programmatic and dynamic creation, configuration and decommissioning of cloud resources on external infrastructures. The benefits of this integration facility for the gCube system are threefold:
- to exploit infrastructural resources in a pay-per-use model
- to scale in/out quickly in response to specific needs
- to reduce manual interventions of Infrastructure Managers.
Contents
Scenarios
- the VRE Manager, according to the demand of data analysis executions in the VRE, decides the number of SmartExecutor nodes needed in the VRE. Through the VRE administration portal, the VRE Manager chooses (from a list of templates) to create the required number of SmartExecutors. She/he chooses on which infrastructure the resources should be created and their characteristics in terms of computation and/or storage capacity. The gCube system, via the integration facility here described, will automatically create the new nodes, register them to the D4Science infrastructure and make them available in the VRE.
- the gCube system intelligently adapt the number of SmartExecutor nodes to the actual demand. In the VRE administration portal, the VRE Manager decides the minimum and maximum number of SmartExecutor expected for the VRE. Then, the gCube system via the integration facility here described, automatically scales-in/out the pool of SmartExecutors (by creating/destroying nodes) predicting the demand for SmartExecutors by analysing VRE accounting and monitoring data.
Requirements
It is possible to recognize the following functionalities that should be available in the integration facilities:
Functional requirements
- Registration and management of cloud providers, access credentials and cloud resources templates on a per-VRE basis. Credentials must be securely stored in the infrastructure;
- Cloud resource lifecycle management. Creation, configuration and decommissioning of cloud resources must be supported. The integration facility allows to use templates for the configuration of cloud resources (e.g. SmartExecutor Template, cpu and memory characteristics);
- Accountability and monitorability. Accounting and monitoring data on usage and workload of resources created on the cloud must be collected and made available in the infrastructure. This is both a requisite to comply with D4Science infrastructure policies and for the automatic scale-in/out;
- User interface. The user interface is integrated in the VRE administration portal since it already contains all the other VRE administration tools
Non-Functional requirements
The solution should have modular architecture in order to support the integration of new cloud providers in a simple and pluggable way.
Non-Functional requiriments
The solution should have modular architecture in order to support the integration of new cloud providers in a simple and pluggable way.
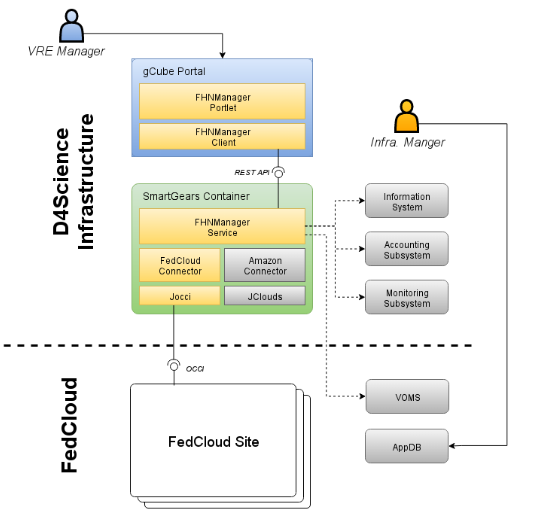
Architecture
The architecture highlights a number of integration-specific components and their interaction among them as well as with existing components, either belonging to the D4Science infrastructure or to the EGI infrastructure. They are described in the subsections above.
Cloud Libraries
Connectors
Federated Hosting Node Manager (FHNM)
Federated Hosting Node Manager Portlet
D4Science Information System
D4Science monitoring system
The Virtual Organization Membership Service (VOMS)
EGI FedCloud sites and AppDB
Service Description
The solution has been developed by means of Java since it is the same technology of the gCube system and it made easier to integrate in the D4Science infrastructure and furthermore there is an high availability for third-party libraries implementing cloud standards.
A brief description of the service is visible in the following subsections.
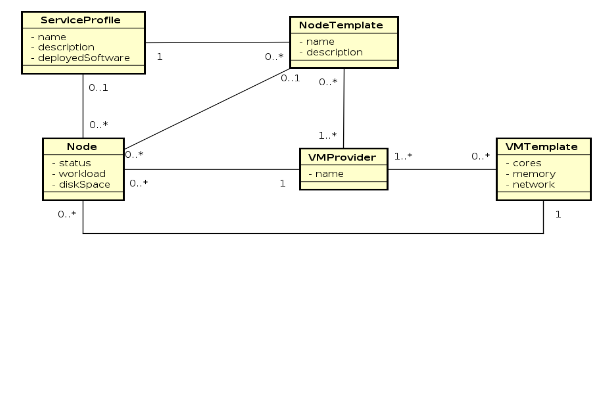
Data Model
FHN Manager
FHN Manager Portlet
Third-party dependencies
- jOCCI: java client library for clouds exposing the OCCI interface released under Apache License Version 2.0
- Jersey: java framework to to realize REST APIs licensed as CDDL Version 1.1 and GPL Version 2
- Liferay 6.0 CE: Enterprise portal framework released under LGPL 2.1
- GWT: Java framework for portlet developing released under Apache License Version 2.0
EGI FedCloud membership
D4Science-FedCloud integration is being tested in the “fedcloud.egi.eu” VO. Production-level operations will be moved to the “d4science.org” VO, registered on the “vomsmania.cnaf.infn.it” VOMS server and in production since December 2015.
Deployment
Components related to the D4Science-FedCloud integration are essentially assembled in two packages that are deployed independently:
- the Federated Hosting Node Manager, embedding cloud libraries and connectors, is deployed in a SmartGears container
- the FHNManagerPortlet is deployed in the gCube portal.
Source Code
The source code of the developed components are available on the gCube code repository.
Datamodel and Common: http://svn.research-infrastructures.eu/d4science/gcube/trunk/vo-management/fhn-manager-api/
Connector: http://svn.research-infrastructures.eu/d4science/gcube/trunk/vo-management/fhn-occi-connector/
FHNManager: http://svn.research-infrastructures.eu/d4science/gcube/trunk/vo-management/fhn-manager-service/
FHN Client Library: http://svn.research-infrastructures.eu/d4science/gcube/trunk/vo-management/fhn-manager-client/
FHNManagerPortlet: http://svn.research-infrastructures.eu/d4science/gcube/trunk/portlets/admin/fhn-manager-portlet/
gCube release and testing process
The software developed to enable the EGI Federated Cloud support in gCube follows the development process and guidelines defined for the whole gCube platform. The platform source code, kept on the project source code repository is continuously built upon each and every change using the ETICS tool. The components have been included in the last gCube release (ver. 3.11.0). Produced packages are available on the public gCube distribution site.
Further documentation
User documentation for the FHNManagerPortlet can be found on the gCube User Guide: https://wiki.gcube-system.org/gcube/User%27s_Guide
FHNManager, connectors and libraries’ API documentation can be found on the gCube Developer’s Guide: https://wiki.gcube-system.org/gcube/Developer%27s_Guide
Deployment and configuration details for the service and the portlet are available on the gCube Administrator’s Guide: https://wiki.gcube-system.org/gcube/Administrator%27s_Guide
License
The FHNManagerPortlet, the FHNManager and the connectors developed within the scope of this task are released under the terms of the European Union Public Licence (EUPL version 1.1), like the rest of the gCube software.