Difference between revisions of "IS-Registry"
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) |
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) (→Removing a GCUBE resource) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The IS-Registry is the gateway to entering in a gCube infrastructure for [[Reference Model#Resource Domain|gCube resources]] by means of registering/unregistering their profiles. | + | == Role == |
| + | |||
| + | The IS-Registry is the gateway to entering in a gCube infrastructure for [[Reference Model#Resource Domain|gCube resources]] by means of registering/unregistering their profiles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The IS-Registry performs three fundamental tasks: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * decide if accept or not a new resource | ||
| + | * validate a resource before its registration | ||
| + | * execute post-deletion actions to keep consistent the IS content | ||
| + | |||
== Design == | == Design == | ||
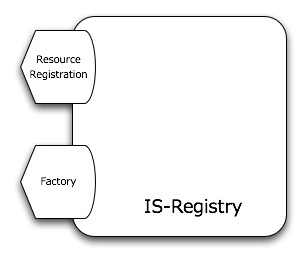
| − | + | The design of the service is distributed across two port-types: the <code>ResourceRegistration</code> and the <code>Factory</code>. Both of them work in a stateless manner, however the Factory creates a stateful resource for notification purposes. | |
| − | [ | + | [[Image:IS-Registry Architecture2.jpg|frame|center|Figure 1. IS-Registry Architecture]] |
| − | == | + | === ResourceRegistration === |
| − | [ | + | [[Image:IS-Registry ResourceRegistration.jpg|frame|center|Figure 2. IS-Registry ResourceRegistration port-type]] |
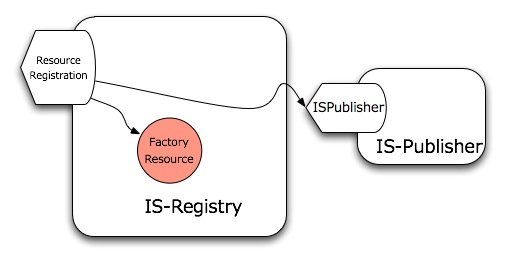
| − | + | The <code>ResourceRegistration</code> port-type manages the registration/update/removal of GCUBE Resources. It is directly contacted only by the [[IS-Publisher]] in order to perform such operations. | |
| − | + | It exposes three operations: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | * [[IS-Registry#Registering_a_new_GCUBE_Resource|<code>create</code>]] – which takes as input a CreateMessage containing the string serialization of the resource profile to register; |
| − | * | + | * [[IS-Registry#Updating_an_existing_GCUBE_Resource|<code>update</code>]] – which takes as input an UpdateMessage containing the new profile that will replace an existing one; |
| − | * ''' | + | * [[IS-Registry#Removing_a_GCUBE_resource|<code>remove</code>]] – which takes as input a RemoveMessage containing the unique identifier of the resource to be removed and its type; |
| + | |||
| + | The first two operations throw an <code>InvalidResourceFault</code> if the profile was not correct/valid and a <code>ResourceNotAcceptedFault</code> if the profile was not accepted because of the instance's configured [[Information_System_Installation#IS_Filters|filters]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Factory === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:IS-Registry Factory.jpg|frame|center|Figure 3. IS-Registry Factory port-type]] | ||
| + | |||
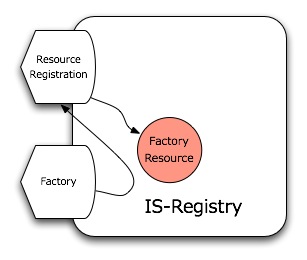
| + | From the functional point of view, the Factory port-type is practically a wrapper around the <code>ResourceRegistration</code> port-type to provide backwards compatibility to previous IS-Publisher and testers implementation. Therefore, it exposes the following operations: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <code>createResource</code> | ||
| + | * <code>updateResource</code> | ||
| + | * <code>removeResource</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | that are mapped on the <code>ResourceRegistration</code>'s operations. | ||
| + | Using this port-type is strongly deprecated and it will likely disappear in the next releases of the service. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === FactoryResource === | ||
| + | |||
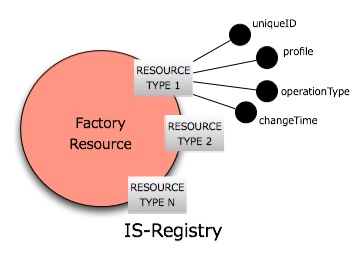
| + | At start up time, the <code>Factory</code> port-type is in charge of creating the singleton <code>FactoryResource</code>. This resource (whose name is derived from previous versions of the service) exposes a set of WS-ResourceProperties registered as Topics in the [[IS-Notifier]], making possible for interested clients to subscribe on events representing the changes of status of Infrastructure constituents (e.g. the disappearance of a Running Instance). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:IS-Registry Resource.jpg|frame|center|Figure 4. IS-Registry FactoryResource]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is the list of RPs exposed: | ||
| + | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| + | <xsd:element name="RegistryFactoryResourceProperties"> | ||
| + | <xsd:complexType> | ||
| + | <xsd:sequence> | ||
| + | <xsd:element ref="tns:RunningInstance" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> | ||
| + | <xsd:element ref="tns:ExternalRunningInstance" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> | ||
| + | <xsd:element ref="tns:Service" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> | ||
| + | <xsd:element ref="tns:Collection" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> | ||
| + | <xsd:element ref="tns:GHN" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> | ||
| + | <xsd:element ref="tns:MetadataCollection" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> | ||
| + | <xsd:element ref="tns:GenericResource" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> | ||
| + | </xsd:sequence> | ||
| + | </xsd:complexType> | ||
| + | </xsd:element> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and each element of the sequence is of type <code>ResourceProperty</code> defined as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="xml"> | ||
| + | <xsd:complexType name="RegistryProperty"> | ||
| + | <xsd:sequence> | ||
| + | <xsd:element name="uniqueID" type="xsd:string" nillable="true"/> | ||
| + | <xsd:element name="profile" type="xsd:string" nillable="true"/> | ||
| + | <xsd:element name="operationType" type="xsd:string" nillable="true"/> | ||
| + | <xsd:element name="changeTime" type="xsd:dateTime" nillable="true"/> | ||
| + | </xsd:sequence> | ||
| + | </xsd:complexType> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that: | ||
| + | * ''uniqueID'' is the identifier of the resource | ||
| + | * ''profile'' is the string serialization of the resource's profile | ||
| + | * ''operationType'' is the type of operation performed on the resource (allowed values are: ''create'', ''update'', ''destroy'') | ||
| + | * ''changeTime'' is the time stamp of the operation | ||
== Sample Usage == | == Sample Usage == | ||
| − | [ | + | This section provides sample usage of the [[IS-Registry#ResourceRegistration|ResourceRegistration]] port-type. The [[IS-Registry#Factory|Factory]] port-type is obsolete and should not be used anymore. |
| + | |||
| + | Note that: | ||
| + | * due to the [[IS-Publisher#Bulked_Publications|behavior]] of the [[IS-Publisher]], any request is executed asynchronously (at the next scheduled bulk execution) | ||
| + | * if the operation is performed inside a service, the ServiceContext has to be used as GCUBESecurityManager (instead of the ''ad hoc'' manager created here below). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Registering a new GCUBE Resource === | ||
| + | The following test method show how to register a new GCUBE Resource: | ||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.CreateMessage; | ||
| + | import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.ResourceRegistrationPortType; | ||
| + | import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.service.ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator; | ||
| + | |||
| + | //... | ||
| + | |||
| + | protected void registerResource(GCUBEResource resource, GCUBEScope scope) throws Exception { | ||
| + | int timeout = 20000; | ||
| + | StringWriter profile = new StringWriter(); | ||
| + | resource.store(profile); | ||
| + | GCUBESecurityManagerImpl manager = new GCUBESecurityManagerImpl() { | ||
| + | public boolean isSecurityEnabled() { return false;} | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator locator = new ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator(); | ||
| + | ResourceRegistrationPortType registration = locator.getResourceRegistrationPortTypePort(epr); | ||
| + | registration = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(registration, scope, timeout, manager); | ||
| + | try { | ||
| + | CreateMessage message = new CreateMessage(); | ||
| + | message.setProfile(profile.toString()); | ||
| + | message.setType(resource.getType()); | ||
| + | registration.create(message); | ||
| + | } catch(Exception e) { | ||
| + | logger.error("Failed to publish the GCUBE Resource ",e); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Updating an existing GCUBE Resource === | ||
| + | The following test method show how to update an existing GCUBE Resource: | ||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.UpdateMessage; | ||
| + | import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.ResourceRegistrationPortType; | ||
| + | import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.service.ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator; | ||
| + | |||
| + | //... | ||
| + | |||
| + | protected void updateResource(GCUBEResource resource, GCUBEScope scope) throws Exception { | ||
| + | int timeout = 20000; | ||
| + | StringWriter profile = new StringWriter(); | ||
| + | resource.store(profile); | ||
| + | GCUBESecurityManagerImpl manager = new GCUBESecurityManagerImpl() { | ||
| + | public boolean isSecurityEnabled() { return false;} | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator locator = new ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator(); | ||
| + | ResourceRegistrationPortType registration = locator.getResourceRegistrationPortTypePort(epr); | ||
| + | registration = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(registration, scope, timeout, manager); | ||
| + | try { | ||
| + | UpdateMessage message = new UpdateMessage(); | ||
| + | message.setUniqueID(profile.getID()); | ||
| + | message.setXmlProfile(profile.toString()); | ||
| + | message.setType(resource.getType()); | ||
| + | registration.update(message); | ||
| + | } catch(Exception e) { | ||
| + | logger.error("Failed to update the GCUBE Resource ",e); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Removing a GCUBE resource === | ||
| + | The following test method show how to remove a GCUBE Resource: | ||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.RemoveMessage; | ||
| + | import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.ResourceRegistrationPortType; | ||
| + | import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.service.ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator; | ||
| + | |||
| + | //... | ||
| + | |||
| + | protected void unregisterResource(GCUBEResource resource, GCUBEScope scope) throws Exception { | ||
| + | int timeout = 20000; | ||
| + | GCUBESecurityManagerImpl manager = new GCUBESecurityManagerImpl() { | ||
| + | public boolean isSecurityEnabled() { return false;} | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator locator = new ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator(); | ||
| + | ResourceRegistrationPortType registration = locator.getResourceRegistrationPortTypePort(epr); | ||
| + | registration = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(registration, scope, timeout, manager); | ||
| + | try { | ||
| + | RemoveMessage message = new RemoveMessage(); | ||
| + | message.setUniqueID(resource.getID()); | ||
| + | message.setType(resource.getType()); | ||
| + | registration.remove(message); | ||
| + | } catch(Exception e) { | ||
| + | logger.error("Failed to remove the GCUBE Resource ",e); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Information System]] | [[Category:Information System]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:51, 9 April 2011
Contents
Role
The IS-Registry is the gateway to entering in a gCube infrastructure for gCube resources by means of registering/unregistering their profiles.
The IS-Registry performs three fundamental tasks:
- decide if accept or not a new resource
- validate a resource before its registration
- execute post-deletion actions to keep consistent the IS content
Design
The design of the service is distributed across two port-types: the ResourceRegistration and the Factory. Both of them work in a stateless manner, however the Factory creates a stateful resource for notification purposes.
ResourceRegistration
The ResourceRegistration port-type manages the registration/update/removal of GCUBE Resources. It is directly contacted only by the IS-Publisher in order to perform such operations.
It exposes three operations:
-
create– which takes as input a CreateMessage containing the string serialization of the resource profile to register; -
update– which takes as input an UpdateMessage containing the new profile that will replace an existing one; -
remove– which takes as input a RemoveMessage containing the unique identifier of the resource to be removed and its type;
The first two operations throw an InvalidResourceFault if the profile was not correct/valid and a ResourceNotAcceptedFault if the profile was not accepted because of the instance's configured filters.
Factory
From the functional point of view, the Factory port-type is practically a wrapper around the ResourceRegistration port-type to provide backwards compatibility to previous IS-Publisher and testers implementation. Therefore, it exposes the following operations:
-
createResource -
updateResource -
removeResource
that are mapped on the ResourceRegistration's operations.
Using this port-type is strongly deprecated and it will likely disappear in the next releases of the service.
FactoryResource
At start up time, the Factory port-type is in charge of creating the singleton FactoryResource. This resource (whose name is derived from previous versions of the service) exposes a set of WS-ResourceProperties registered as Topics in the IS-Notifier, making possible for interested clients to subscribe on events representing the changes of status of Infrastructure constituents (e.g. the disappearance of a Running Instance).
This is the list of RPs exposed:
<xsd:element name="RegistryFactoryResourceProperties"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element ref="tns:RunningInstance" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> <xsd:element ref="tns:ExternalRunningInstance" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> <xsd:element ref="tns:Service" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> <xsd:element ref="tns:Collection" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> <xsd:element ref="tns:GHN" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> <xsd:element ref="tns:MetadataCollection" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> <xsd:element ref="tns:GenericResource" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element>
and each element of the sequence is of type ResourceProperty defined as follows:
<xsd:complexType name="RegistryProperty"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="uniqueID" type="xsd:string" nillable="true"/> <xsd:element name="profile" type="xsd:string" nillable="true"/> <xsd:element name="operationType" type="xsd:string" nillable="true"/> <xsd:element name="changeTime" type="xsd:dateTime" nillable="true"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType>
Note that:
- uniqueID is the identifier of the resource
- profile is the string serialization of the resource's profile
- operationType is the type of operation performed on the resource (allowed values are: create, update, destroy)
- changeTime is the time stamp of the operation
Sample Usage
This section provides sample usage of the ResourceRegistration port-type. The Factory port-type is obsolete and should not be used anymore.
Note that:
- due to the behavior of the IS-Publisher, any request is executed asynchronously (at the next scheduled bulk execution)
- if the operation is performed inside a service, the ServiceContext has to be used as GCUBESecurityManager (instead of the ad hoc manager created here below).
Registering a new GCUBE Resource
The following test method show how to register a new GCUBE Resource:
import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.CreateMessage; import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.ResourceRegistrationPortType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.service.ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator; //... protected void registerResource(GCUBEResource resource, GCUBEScope scope) throws Exception { int timeout = 20000; StringWriter profile = new StringWriter(); resource.store(profile); GCUBESecurityManagerImpl manager = new GCUBESecurityManagerImpl() { public boolean isSecurityEnabled() { return false;} }; ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator locator = new ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator(); ResourceRegistrationPortType registration = locator.getResourceRegistrationPortTypePort(epr); registration = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(registration, scope, timeout, manager); try { CreateMessage message = new CreateMessage(); message.setProfile(profile.toString()); message.setType(resource.getType()); registration.create(message); } catch(Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to publish the GCUBE Resource ",e); } }
Updating an existing GCUBE Resource
The following test method show how to update an existing GCUBE Resource:
import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.UpdateMessage; import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.ResourceRegistrationPortType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.service.ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator; //... protected void updateResource(GCUBEResource resource, GCUBEScope scope) throws Exception { int timeout = 20000; StringWriter profile = new StringWriter(); resource.store(profile); GCUBESecurityManagerImpl manager = new GCUBESecurityManagerImpl() { public boolean isSecurityEnabled() { return false;} }; ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator locator = new ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator(); ResourceRegistrationPortType registration = locator.getResourceRegistrationPortTypePort(epr); registration = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(registration, scope, timeout, manager); try { UpdateMessage message = new UpdateMessage(); message.setUniqueID(profile.getID()); message.setXmlProfile(profile.toString()); message.setType(resource.getType()); registration.update(message); } catch(Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to update the GCUBE Resource ",e); } }
Removing a GCUBE resource
The following test method show how to remove a GCUBE Resource:
import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.RemoveMessage; import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.ResourceRegistrationPortType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.registry.stubs.resourceregistration.service.ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator; //... protected void unregisterResource(GCUBEResource resource, GCUBEScope scope) throws Exception { int timeout = 20000; GCUBESecurityManagerImpl manager = new GCUBESecurityManagerImpl() { public boolean isSecurityEnabled() { return false;} }; ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator locator = new ResourceRegistrationServiceAddressingLocator(); ResourceRegistrationPortType registration = locator.getResourceRegistrationPortTypePort(epr); registration = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(registration, scope, timeout, manager); try { RemoveMessage message = new RemoveMessage(); message.setUniqueID(resource.getID()); message.setType(resource.getType()); registration.remove(message); } catch(Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to remove the GCUBE Resource ",e); } }