Difference between revisions of "VO Resources"
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) (→Mandatory VO Resources) |
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) (→Optional VO Resources) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
The following resources can be optionally registered in a VO scope: | The following resources can be optionally registered in a VO scope: | ||
| − | * ISFilters | + | * ISFilters: a set of filters can be configured in order to prevent the publication of some GCUBEResources matching the given criteria. The IS-Registry instance uses the [[Information_System_Installation#IS_Filters|ISFilters]] resource to ... |
| − | + | * AIS scripts | |
=== How to Register VO Resources === | === How to Register VO Resources === | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 3 December 2009
Several VO-level services require specific configuration at VO scope in order to be functional. This “Configuration” is modelled as a gCube Resource and kept in the Information System.
Each resource is a centralized configuration unit called Generic Resource. The payload is usually a service-specific XML and new (not currently existing) services can register their own generic resources.
There exist mandatory VO Resources and optional VO Resources. Many of the mandatory resources are prerequisites for the bootstrapping process of the Information Retrieval area.
Mandatory VO Resources
The following resources are mandatory to be registered in any VO scope:
- VRE Modeler resource: this resource is used at VRE Definition time. A VRE Designer can easily generate new VREs through the VRE Definition portlet; here, she/he selects the functionalities (portlets and services) that will be made available to the VRE users, from the list of available functionalities in the VO. This list of VO functionalities presented to the VRE Designer is stored in the VRE Modeler resource;
- Transformation Programs: the Metadata Broker and gDTS services provide the functionality to transform various types of data to other formats. A Transformation Program resource describes details about a specific transformation that can be applied to a Metadata Schema format. The transformation services use these resources in order to understand how the input data should be handled and transformed;
- Transformation programs: the Metadata Broker and gDTS services provide the functionality to transform various types of data to other formats. Details about such transformations are described in Transformation Program resources, in a XML-based syntax. The transformation services use these resources in order to understand how the input data should be handled and transformed. Transformations can be:
- XSLT-based (only for XML data)
- Custom (using plain java code or external libraries/applications)
- A combination of the previous methods
- Transformation XSLTs: XSLT-based Transformation Programs do not contain the XSLT definitions inside them. XSLTs are stored as separate transformation XSLT resources. Transformation Programs contain only references to the transformation XSLT resources;
- Index types: the gCube index services (more on them later) can index various forms of XML data, as long as a description of the structure of the data is given and there is no ‘fixed’ schema for the indexed data. The structure description and details about how the data should be indexed is stored inside index type resources. There are three types of index type resources:
- Full text index type
- Geo index type
- Forward index type
- IRBootstrapper configuration: this resource provides configuration details for the operation of the IRBootstrapper portlet;
- Default User Profile: each user of the system has a profile associated with him/her for each VO. However, When a user logs in a VO for the first time, such a profile does not exist. A profile that contains default values for the various user preferences and settings is automatically created for the particular VO. The contents of this profile are copied from the Default User Profile resource;
- Metadata XSLTs: the portal needs to present the metadata of information objects to the user in a nicely formatted and user-friendly way. Metadata XSLT resources contain the transformation that is applied on the XML metadata in order to produce a nicely formatted representation. One metadata XSLT resource must be defined for each metadata schema used in the VO;
- Presentation XSLTs: when a user performs a search through the portal, a small fragment of the object’s metadata is displayed for each matching object. Presentation XSLT resources contain the transformation that is applied on the XML metadata in order to produce this fragment. One presentation XSLT resource must be defined for each metadata schema used in the VO;
- Metadata schema info: the portal needs to have some knowledge about the searchable fields for each collection in the VO. This information is given through the metadata schema info resources. There is one resource for each different metadata schema available in the VO;
- Portal layout: the portal supports different portlet layouts per VO and per VRE. Portal layout resources define the layout to be used when a user logs in a VO. The information reported there are: (i) portlets to be displayed and (ii) how each portlet is displayed (tab organization);
Optional VO Resources
The following resources can be optionally registered in a VO scope:
- ISFilters: a set of filters can be configured in order to prevent the publication of some GCUBEResources matching the given criteria. The IS-Registry instance uses the ISFilters resource to ...
- AIS scripts
How to Register VO Resources
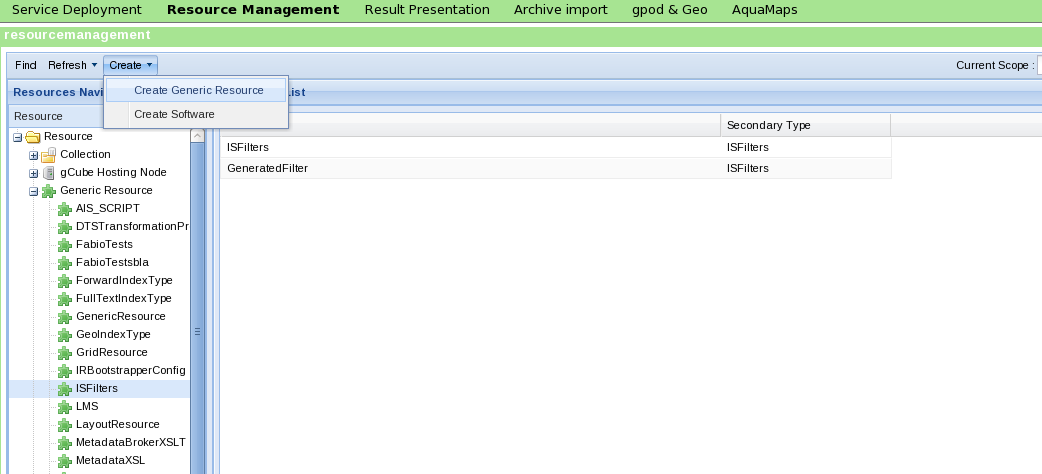
At gCube Information System (shortly, IS) level, all the VO Resources are classified as Generic Resources and can be easily managed trough a graphical user interface. The Resource Management portlet is an advanced tool for managing any kind of resource stored in the IS. This portlet is available at VO level, when a user with VO-Admin role logs on in the VO trough the Portal.
In order to create and register a new Generic Resource, the Create Generic Resource item from Main menu must be selected as shown in the following figure.
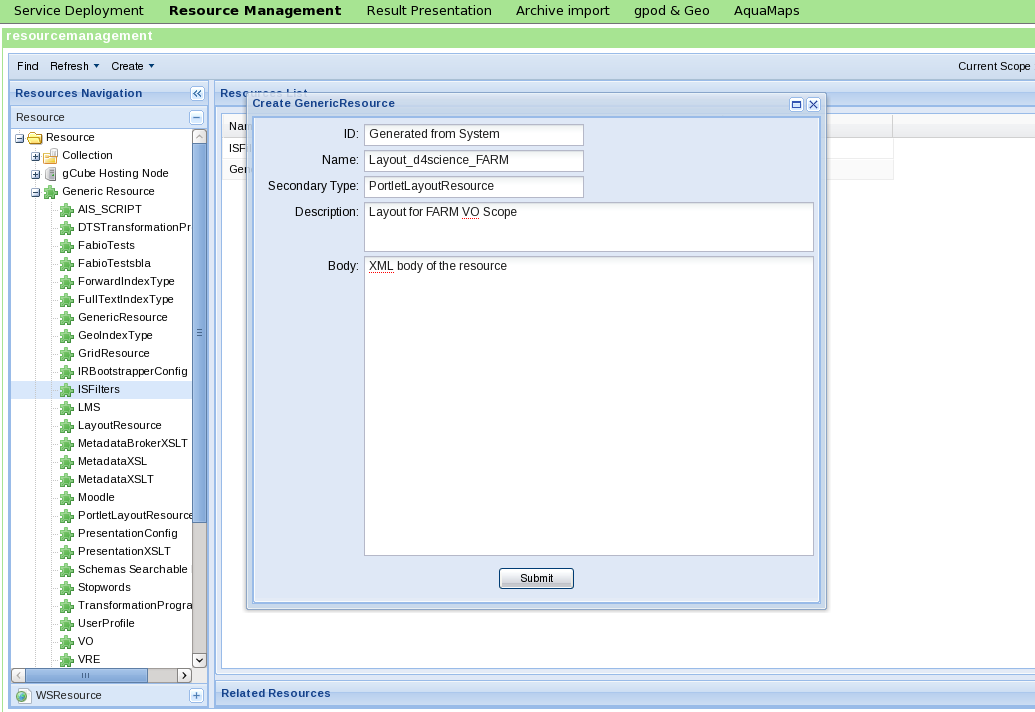
Then, the following form pops up:
By filling all the fields with the appropriate values (depending on the to-be-registered resource's semantic, of course) and clicking submit, the new Generic Resource is stored in the IS and automatically joined to the current VO scope.