Difference between revisions of "IS-Collector"
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) (→Operation: addSubcollection) |
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) (→Querying the data) |
||
| Line 483: | Line 483: | ||
=== XQueryAccess portType === | === XQueryAccess portType === | ||
| − | ===== | + | ===== Operation: XQueryExecute ===== |
| − | The <code>XQueryExecute</code> operation | + | The <code>XQueryExecute</code> operation allows to send XQuery to the service that are executed on the eXist instance. |
| + | |||
| + | The operation can be invoked as follows: | ||
<source lang="java"> | <source lang="java"> | ||
| Line 505: | Line 507: | ||
import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.service.XQueryAccessServiceLocator; | import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.service.XQueryAccessServiceLocator; | ||
| − | / | + | //... |
| − | + | String portTypeURI = "http://"+args[0]+":"+ args[1]+"/wsrf/services/gcube/informationsystem/collector/XQueryAccess"; | |
| − | + | String xQueryExpression = ...; | |
| − | + | XQueryAccessPortType port = null; | |
| − | + | try { | |
| − | + | port = new XQueryAccessServiceLocator().getXQueryAccessPortTypePort(new URL(portTypeURI)); | |
| − | + | port = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(port, GCUBEScope.getScope(args[2])); | |
| − | + | } catch (Exception e) { | |
| − | + | logger.error(e); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | XQueryExecuteRequest request = new XQueryExecuteRequest(); | |
| − | + | request.setXQueryExpression(xQueryExpression); | |
| − | + | try { | |
| − | + | XQueryExecuteResponse response = port.XQueryExecute(request); | |
| − | + | logger.info("Number of returned records: " + response.getSize()); | |
| − | + | logger.info("Dataset: \n" + response.getDataset()); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | } catch (XQueryFaultType e) { | |
| − | + | logger.error("XQuery Fault Error received", e); | |
| − | + | } catch (RemoteException e) { | |
| − | + | logger.error(e); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | </source> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The operation returns in a single string object all the records satisfying the query. The results are formatted in this way: | |
| − | + | <source lang="xml"> | |
| + | <Resultset> | ||
| + | <Record> | ||
| + | <!-- first record --> | ||
| + | </Record> | ||
| + | <Record> | ||
| + | <!-- second record --> | ||
| + | </Record> | ||
| + | <!-- other records --> | ||
| + | </Resultset> | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Revision as of 05:36, 13 April 2011
Contents
Role
The IS-InformationCollector is a gCube service in charge of aggregating the information published by the gCube services belonging an infrastructure or a subset of it (this depends on the infrastructure configuration).
Major features of the service are:
- storage, indexing, and management of gCube Resources profiles
- storage, indexing, and management of instances' states in the form of WS-ResourceProperties documents
- storage, indexing, and management of well-formed XML documents
- full XQuery 1.0 support over the collected information
- remote management of the underlying XMLStorage
It plays a crucial role on an infrastructure, since it provides to clients a continuously updated picture of the infrastructure and its state. Responsiveness is also a key point of the service: many queries are sent to the InformationCollector during online operations and any delay introduces by the query processing is immediately reflected on any aspect of the system.
Historically, the service was conceived as an aggregator service, able to create Aggregator Sinks that query remote Aggregator Sources (in particular QueryAggregatorSources, as those created by the IS-Publisher) to harvest resource properties.
Version 3.0 features a new WS-DAIX compliant interface proving a more general approach to the feeding phase.
Documents
As wrote, IS-InformationCollector is capable to handle three class of documents. Two of them, gCube Resource profiles and instance's states, have a specific semantic in the infrastructure since:
- gCube Resource profiles are the manifestation of gCube Resource and allow interested client to discover such resources
- instance's states, in the form of WS-ResourceProperties document, are views on the state of instance of gCube services
Because of this semantic, the two classes of resource require some extra-information for their correct management. In particular, the to-be-stored documents has to come along with a metadata record reporting information about the publisher and the resource lifetime. The record must have the following structure:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <Metadata> <Type>Profile|InstanceState</Type> <Source>URI</Source> <TimeToLive>600</TimeToLive> <GroupKey>MyGroupKey</GroupKey> <EntryKey>MyEntryKey</EntryKey> <Key>MyKey</Key> <Namespace>URI </Namespace> <PublicationMode>push|pull<7PublicationMode> </Metadata>
It gives to the service the information about:
- the type of the resource (Profile or Instance State)
- the URL of the publisher service (Source)
- the lifetime (TimeToLive) of the resource in seconds, which is added to the time the service receives the document (this is valid only for instance states published in push mode)
- the service group resource, identified by the GroupKey and EntryKey element (this is valid only for instance states published through the Sink port-type)
- the namespace of the WSDL in which the resource was defined (this is valid only for instance states)
- the publication mode, push if the resource is pushed at each change, pull if it is periodically sent to the service (this is valid only for instance states)
This information are then wrapped around the source document and indexed.
The resulting document looks like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Document>
<ID>3bb6e850-94d2-11df-8d06-8e825c7c7b8d</ID>
<Source>http://source</Source>
<SourceKey>MyKey</SourceKey>
<CompleteSourceKey/>
<EntryKey>MyEntryKey</EntryKey>
<GroupKey>MyGroupKey</GroupKey>
<TerminationTime>1288103198680</TerminationTime>
<TerminationTimeHuman>Tue Oct 26 15:26:38 GMT+01:00 2010</TerminationTimeHuman>
<LastUpdateMs>1288102598680</LastUpdateMs>
<LastUpdateHuman>Tue Oct 26 15:16:38 GMT+01:00 2010</LastUpdateHuman>
<Data>
<Resource xmlns="" version="0.4.x">
<ID>...</ID>
<Type>...</Type>
<Scopes>
<Scope>...</Scope>
</Scopes>
<Profile>
<!-- the profile section is here -->
</Profile>
</Resource>
</Data>
</Document>
This allows to:
- have more enriched queries based also on the publisher's data
- manage the termination time of the resource by relying on the time machine of the node hosting the Collector instance (the TimeToLive in seconds is added to the last update time in order to obtain an absolute expiration time of the document), by avoiding problems due to different timezones in the infrastructure.
About the target collection in which the document will be stored:
- the collection is automatically derived (and created, if needed) starting from the document type and the information included in the document itself
- the collection name reported in the invocation to the AddDocuments operation is therefore ignored
If a document comes alone, i.e. without a metadata record, it is treated as a generic XML documents and stored in the target collection indicated in the addDocuments invocation.
XML Indexing
The IS-InformationCollector uses an embedded instance of eXist 1.2 to index XML data according to the XML data model and offers efficient, index-based XQuery processing. The documents are stored in collections following this structure:
gcube:// | |- Profiles | |-<type1> | |-<type2> | |- .. | |-<typeN> | |- Properties | |- <User defined collection(s)> | |- <User defined sub-collection(s)>
Profiles and Properties collections are reserved to store respectively gCube resource's profiles and instance's states. Under the Profiles collection, a sub-collection with the resource type name is created whenever a new type is detected in a to-be-stored profile. Moreover, a client may define his own structure of collection and sub-collections and store, index and query there his documents via the XMLCollectionAccess port-type. This hierarchy of collections and sub-collections must be kept in mind when constructing a query expression to execute via the XMLQueryAccess.
Periodic exports (as zipped archives) of the XML database content are performed for backup purposes. The behavior of this activity can be configured in the JNDI file. The following section of the JNDI file shows the parameters that may be used to define where, when and how many backups are managed:
<service name="gcube/informationsystem/collector"> <!-- ... --> <environment name="backupDir" value="existICBackups" type="java.lang.String" override="false" /> <environment name="maxBackups" value="10" type="java.lang.String" override="false" /> <environment name="scheduledBackupInHours" value="12" type="java.lang.String" override="false" /> </service>
In this example, backups are done every 12 hours and stored under the $HOME/.gcore/... /existICBackups folder. 10 backups are maintained and when a new one is available, the oldest one is discarded. If an absolute path is indicated as backupDir, the backups are not stored under the gCore persistent folder.
Design
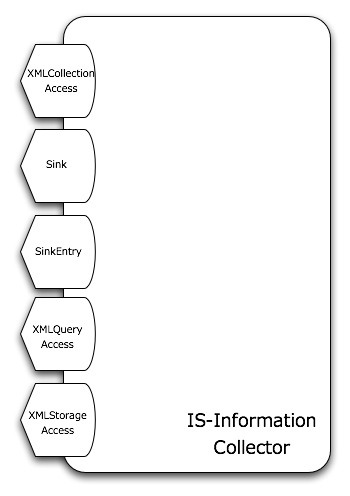
The functionalities delivered by the service are logically organized across 5 port-types:
where:
- XMLCollectionAccess, Sink and SinkEntry are dedicated to the publishing phase
- XMLQueryAccess allows to execute XQuery expression over the instance's content
- XMLStorageAcess is used to remotely manage the XML Storage underlying the service instance
XMLCollectionAccess port-type
The XMLCollectionAccess port-type has been added from version 3.0 on of the InformationCollector. It defines the feeding phase of the service following the the XML Realization (WS-DAIX) Specification, Version 1.0 of the Web Services Data Access and Integration. It exposes the following operations:
-
addDocuments -
removeDocuments -
getDocuments -
createSubcollection -
removeSubcollection -
addSchema -
removeSchema
Each operation works on the embedded XML database instance to satisfy the client's request. The last two operations (addSchema and removeSchema) throw a NotAuthorizedFaultType because schema are not supported in version 3.0.
Note that the removeSubcollection operation removes the entire content of the selected subcollection.
Operation: addDocuments
The addDocuments operation accepts a list of new XML documents and eventually a list (of the same cardinality) of metadata records. An existing target Collection must be also specified in case of generic XML documents.
Interaction with the addDocuments operation is illustrated with the example below:
import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdai.DataResourceUnavailableFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdai.InvalidResourceNameFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdai.NotAuthorizedFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdai.ServiceBusyFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.AddDocumentRequestWrapper; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.AddDocumentsRequest; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.AddDocumentsResponse; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.InvalidCollectionNameFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.XMLCollectionAccessPT; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.XMLWrapperType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.service.WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator; import org.w3c.dom.Document; //... protected static void invokeAddDocuments(String host, int port, GCUBEScope scope, URI collectionURI, String[] documentNames, Document[] documents, Document[] metadata) throws Exception { String portTypeURI = "http://" + host + ":" + port + "/wsrf/services/gcube/informationsystem/collector/wsdaix/XMLCollectionAccess"; XMLCollectionAccessPT sink = null; try { sink = new WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator().getXMLCollectionAccessPTPort(new URL(portTypeURI)); sink = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(stubs, scope); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to create the port-type instance", e); } logger.trace("Sending resource to " + sink.getAddress().toString()); AddDocumentsRequest request = new AddDocumentsRequest(); request.setDataResourceAbstractName(new org.apache.axis.types.URI("gcube://unused")); AddDocumentRequestWrapper[] wrappers = new AddDocumentRequestWrapper[documentNames.length]; for (int i=0; i < documentNames.length; i++) { wrappers[i] = new AddDocumentRequestWrapper(); wrappers[i].setDocumentName(documentNames[i]); XMLWrapperType wrapper = new XMLWrapperType(); MessageElement msgElement = new MessageElement(Constants.CORE_NS, "ISPublisher", documents[i]); msgElement.setType(org.apache.axis.Constants.XSD_ANYTYPE); if (metadata != null) { MessageElement msgElement2; try { msgElement2 = new MessageElement(Constants.CORE_NS, "ISPublisher", metadata[i].getDocumentElement()); msgElement2.setType(org.apache.axis.Constants.XSD_ANYTYPE); wrapper.set_any(new MessageElement[] { msgElement, msgElement2 }); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Unable to add the document metadata for " + documentNames[i], e); throw e; } } else { wrapper.set_any(new MessageElement[] { msgElement }); } wrappers[i].setData(wrapper); } request.setAddDocumentRequestWrapper(wrappers); request.setCollectionName(collectionURI); XMLCollectionAccessPT stubs = null; try { stubs = new WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator().getXMLCollectionAccessPTPort(sink); stubs = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(stubs, scope, getTimeout()); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to add document " + documentNames[0], e); } AddDocumentsResponse response = stubs.addDocuments(request); logger.trace("Number of response wrappers " + response.getAddDocumentResponseWrapper().length); String sresponse = null; for (int i = 0; i < response.getAddDocumentResponseWrapper().length; i++) { sresponse = response.getAddDocumentResponseWrapper()[i].getResponse().toString(); logger.trace("Returned response for " + response.getAddDocumentResponseWrapper()[i].getDocumentName() + ": " + sresponse); } return; }
For each document, the addDocuments operation returns one of the following response wrapper values:
- Success, if the document was accepted and indexed
- DocumentNotAdded-DocumentDoesNotValidate , if the document was not compliant with the schema associated to the target collection (actually not used)
- DocumentNotAdded-SchemaDoesNotExist, if the target collection did not have an associated schema (actually not used)
- DocumentNotAdded-NotAuthorized, if the client did not have the right to store that document in the target collection
- DocumentOfSameNameOverwritten, if a document with the same name already exist and was replaced
Adding an Instance State
In order to add a new instance state, the related metadata record has to be created firstly. For this purpose, the MetadataWriter utility distributed with the IC stubs can be used:
import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.metadata.MetadataRecord; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.metadata.MetadataWriter; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.metadata.MetadataRecord.TYPE; import org.w3c.dom.Document; //... GCUBEWSResource resource = ... ; MetadataWriter writer = new MetadataWriter(TYPE.INSTANCESTATE, resource.getEPR().getAddress().toString(), //URI of the service to which the resource belongs to 600, //time to live in seconds "groupkey", //unused field resource.getID().getValue(), //resource id "entrykey", //unused field resource.getID().getName().getNamespaceURI(), //resource namespace as defined in the WSDL "push"); //publication mode Document metadata = writer.getRecord().getAsDocument();
Then, the invokeAddDocuments method (illustrated above) can be invoked as follows:
GCUBEWSResource resource = ...; GCUBEScope scope = ...; //... invokeAddDocuments(<host>, <port> scope, new org.apache.axis.types.URI("gcube://properties"), new String[]{resource.getID()}, new Document[]{resource.getDocument()}, new Document[]{metadata});
Adding a gCube Resource profile
As in the previous case, the metadata record has to be created firstly with the MetadataWriter utility:
import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.metadata.MetadataRecord; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.metadata.MetadataWriter; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.metadata.MetadataRecord.TYPE; import org.w3c.dom.Document; //... GCUBEWSResource resource = ... ; MetadataWriter writer = new MetadataWriter(TYPE.GCUBERESOURCE, GHNContext.getContext().getBaseURL(), // the source gHN 0 //time to live in seconds ); Document metadata = writer.getRecord().getAsDocument();
Then, the invokeAddDocuments method (illustrated above) can be invoked as follows:
import java.io.StringReader; import java.io.StringWriter; import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder; import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory; import org.gcube.common.core.resources.GCUBEResource; //... GCUBEResource resource = ...; GCUBEScope scope = ...; StringWriter writer = new StringWriter(); resource.store(writer); DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); factory.setNamespaceAware(true); DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder(); StringReader reader = new StringReader(writer.toString()); invokeAddDocuments(<host>, <port> scope, new org.apache.axis.types.URI("gcube://profiles/"+resource.getType()), new String[]{resource.getID()}, new Document[]{builder.parse(new InputSource(reader))}, new Document[]{metadata});
Adding an XML document
Adding a new XML document does not require an associated metadata record. The only constrain is that the target collection must be previously created with the createSubcollection operation.
The following simple invocation to the invokeAddDocuments method (defined above) shows how to add a new XML document:
import org.w3c.dom.Document; //... Document document = ...; String id = "myID"; String myCollectionName = "parent/child"; invokeAddDocuments(<host>, <port> scope, new org.apache.axis.types.URI("gcube://" + myCollectionName), new String[]{id}, new Document[]{document}, null;
Operation: removeDocuments
This operation allows to remove a list of documents from a collection.
The following method shows how to invoke the removeDocuments operation:
import org.apache.axis.types.URI; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdai.DataResourceUnavailableFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdai.InvalidResourceNameFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdai.NotAuthorizedFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdai.ServiceBusyFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.InvalidCollectionNameFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.RemoveDocumentRequestWrapper; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.RemoveDocumentResponseWrapper; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.RemoveDocumentsRequest; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.RemoveDocumentsResponse; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.XMLCollectionAccessPT; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.XMLWrapperType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.service.WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator; //... protected static void invokeRemoveDocuments(String host, int port, sink, GCUBEScope scope, URI collectionURI, String[] documentNames) throws DataResourceUnavailableFaultType, MalformedURLException, RemoteException, ServiceBusyFaultType, InvalidResourceNameFaultType, InvalidCollectionNameFaultType, NotAuthorizedFaultType { String portTypeURI = "http://" + host + ":" + port + "/wsrf/services/gcube/informationsystem/collector/wsdaix/XMLCollectionAccess"; XMLCollectionAccessPT sink = null; try { sink = new WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator().getXMLCollectionAccessPTPort(new URL(portTypeURI)); sink = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(stubs, scope); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to create the port-type instance", e); } logger.trace("Removing document from " + sink.getAddress().toString()); RemoveDocumentsRequest request = new RemoveDocumentsRequest(); request.setDataResourceAbstractName(new org.apache.axis.types.URI("gcube://unused"); RemoveDocumentRequestWrapper[] wrappers = new RemoveDocumentRequestWrapper[documentNames.length]; for (int i = 0; i < documentNames.length; i++) { wrappers[i] = new RemoveDocumentRequestWrapper(); wrappers[i].setDocumentName(documentNames[i]); } request.setRemoveDocumentRequestWrapper(wrappers); request.setCollectionName(collectionURI); XMLCollectionAccessPT stubs = null; try { stubs = new WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator().getXMLCollectionAccessPTPort(sink); stubs = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(stubs, scope, getTimeout()); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to remove the resource", e); } RemoveDocumentsResponse response = stubs.removeDocuments(request); RemoveDocumentResponseWrapper[] rwrappers = response.getRemoveDocumentResponseWrapper(); for (RemoveDocumentResponseWrapper wrapper : rwrappers) { logger.trace("Document name " + wrapper.getDocumentName()); logger.trace("Returned response from remove operation " + wrapper.getResponse().toString()); XMLWrapperType detail = wrapper.getDetail(); } return; }
For each document, the removeDocuments operation returns one of the following response wrapper values:
- Success, if the document was successfully removed
- DocumentNotRemoved-NotAuthorized, if the caller does not have the right to remove the document
- documentDoesNotExist, if the document does not exist
Operation: addSubcollection
Creating sub-collections is extremely easy. Sub-collections must be always created under a parent collection. The InformationCollector defines all the collection under the gcube:// schema. If a collection is at the top of the hierarchy, it is a child of the // collection, otherwise the parent collection must be indicated (e.g.: gcube://parentCollectionName).
The following code shows how to invoke the addSubcollection operation:
import org.apache.axis.types.URI; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.CreateSubcollectionRequest; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.XMLCollectionAccessPT; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.service.WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator; //... String portTypeURI = "http://" + host + ":" + port + "/wsrf/services/gcube/informationsystem/collector/wsdaix/XMLCollectionAccess"; String collectionName = "mycollection"; GCUBEScope scope = ...; try { CreateSubcollectionRequest request = new CreateSubcollectionRequest(); request.setDataResourceAbstractName(new URI("gcube://unused")); request.setCollectionName(new URI("gcube://")); //collectionName will be placed under the root collection request.setSubcollectionName(new URI("gcube://" + collectionName)); XMLCollectionAccessPT stubs = new WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator().getXMLCollectionAccessPTPort(new URL(portTypeURI)); stubs = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(stubs, scope); stubs.createSubcollection(request); logger.info("Subcollection successfully created"); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to create subcollection " + collectionName, e); }
Operation: removeSubcollection
A sub-collection is removed following the same logic of its creation. Keep in mind that if the collection is not empty, its entire content will be deleted.
The following code shows how to invoke the removeSubcollection operation:
import org.apache.axis.types.URI; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.RemoveSubcollectionRequest; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.XMLCollectionAccessPT; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.wsdaix.service.WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator; //... String portTypeURI = "http://" + host + ":" + port + "/wsrf/services/gcube/informationsystem/collector/wsdaix/XMLCollectionAccess"; String collectionName = "mycollection"; GCUBEScope scope = ...; try { RemoveSubcollectionRequest request = new RemoveSubcollectionRequest(); request.setDataResourceAbstractName(new URI("gcube://unused")); request.setCollectionName(new URI("gcube://")); request.setSubcollectionName(new URI("gcube://" + collectionName)); XMLCollectionAccessPT stubs = new WsdaixServiceAddressingLocator().getXMLCollectionAccessPTPort(new URL(portTypeURI)); stubs = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(stubs, scope); stubs.removeSubcollection(request); logger.info("Subcollection successfully removed"); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to remove subcollection " + collectionName, e); }
XQueryAccess portType
Operation: XQueryExecute
The XQueryExecute operation allows to send XQuery to the service that are executed on the eXist instance.
The operation can be invoked as follows:
package org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.testsuite; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URL; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import org.gcube.common.core.contexts.GCUBERemotePortTypeContext; import org.gcube.common.core.scope.GCUBEScope; import org.gcube.common.core.utils.logging.GCUBEClientLog; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.XQueryAccessPortType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.XQueryExecuteRequest; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.XQueryExecuteResponse; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.XQueryFaultType; import org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.stubs.service.XQueryAccessServiceLocator; //... String portTypeURI = "http://"+args[0]+":"+ args[1]+"/wsrf/services/gcube/informationsystem/collector/XQueryAccess"; String xQueryExpression = ...; XQueryAccessPortType port = null; try { port = new XQueryAccessServiceLocator().getXQueryAccessPortTypePort(new URL(portTypeURI)); port = GCUBERemotePortTypeContext.getProxy(port, GCUBEScope.getScope(args[2])); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error(e); } XQueryExecuteRequest request = new XQueryExecuteRequest(); request.setXQueryExpression(xQueryExpression); try { XQueryExecuteResponse response = port.XQueryExecute(request); logger.info("Number of returned records: " + response.getSize()); logger.info("Dataset: \n" + response.getDataset()); } catch (XQueryFaultType e) { logger.error("XQuery Fault Error received", e); } catch (RemoteException e) { logger.error(e); }
The operation returns in a single string object all the records satisfying the query. The results are formatted in this way:
<Resultset> <Record> <!-- first record --> </Record> <Record> <!-- second record --> </Record> <!-- other records --> </Resultset>
Sample queries
...
Sink portType
Registering a new resource
A sample registration file:
<ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters xmlns:sgc="http://mds.globus.org/servicegroup/client" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:wsa="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/03/addressing" xmlns:agg="http://mds.globus.org/aggregator/types" xmlns="http://mds.globus.org/servicegroup/client"> <!-- Specifies that the registration will be renewed every 60 seconds --> <RefreshIntervalSecs>60</RefreshIntervalSecs> <!-- <Content> specifies registration specific information --> <Content xsi:type="agg:AggregatorContent" xmlns:agg="http://mds.globus.org/aggregator/types"> <agg:AggregatorConfig> <agg:GetMultipleResourcePropertiesPollType xmlns:metadatamanager="http://gcube-system.org/namespaces/metadatamanagement/metadatamanager"> <!-- Polling interval --> <agg:PollIntervalMillis>60000</agg:PollIntervalMillis> <!-- Resource names--> <agg:ResourcePropertyNames>metadatamanager:MetadataCollectionID</agg:ResourcePropertyNames> <agg:ResourcePropertyNames>metadatamanager:LastUpdateTime</agg:ResourcePropertyNames> </agg:GetMultipleResourcePropertiesPollType> </agg:AggregatorConfig> <agg:AggregatorData/> </Content> </ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters>
A sample Registration class:
import org.globus.wsrf.encoding.ObjectDeserializer; import org.globus.wsrf.impl.servicegroup.client.ServiceGroupRegistrationClient; import org.globus.wsrf.impl.servicegroup.client.ServiceGroupRegistrationClientCallback; import org.globus.wsrf.utils.XmlUtils; import org.globus.mds.servicegroup.client.ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters; import org.apache.axis.message.addressing.EndpointReferenceType; import commonj.timers.Timer; /** * Registration class for Aggregator Resources * * @author Manuele Simi (ISTI-CNR) * */ public class Registration implements ServiceGroupRegistrationClientCallback { private final EndpointReferenceType source; // the SOURCE endpoint private final EndpointReferenceType sink; // the SINK endpoint, e.g. http://dlib27.isti.cnr.it:8000/wsrf/services/gcube/informationsystem/collector/Sink private String registrationFile = "...";// the content of the registration file public void register() { byte[] bArray = this.registrationFile.getBytes(); ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(bArray); Document doc = XmlUtils.newDocument(bais); // setting parameters for this registration ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters params = (ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters) ObjectDeserializer.toObject(doc.getDocumentElement(), ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters.class); params.setRegistrantEPR(this.source); params.setServiceGroupEPR(this.sink); // create a serviceGroupRegistration Client for registration ServiceGroupRegistrationClient client = new ServiceGroupRegistrationClient(); // subscribe to receive registration status messages client.setClientCallback(this); /* * The client creates a SinkEntry in the appropriate target WS-ServiceGroup. Then, it periodically attempts to renew WS-ResourceLifetime lifetime extension on the * SinkEntry. If the client detects that the SinkEntry no longer available, it will create a new one. */ Timer timer = client.register(params, 1000); } /** * {@inheritDoc} * @see org.globus.wsrf.impl.servicegroup.client.ServiceGroupRegistrationClientCallback#setRegistrationStatus( * org.globus.mds.servicegroup.client.ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters, boolean, boolean,java.lang.Exception) */ public boolean setRegistrationStatus(ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters regParams, boolean wasSuccessful, boolean wasRenewalAttempt, Exception exception) { if (wasSuccessful) { if (wasRenewalAttempt) { logger.trace("Renewal of the existing registration completed successfully"); } else { logger.trace("New registration completed successfully"); } } else { logger.error("Registration failed"); } } }
Test-suite
The IS-Collector comes with a test-suite package allowing to test its administration functionalities (mainly the XMLStorageAccess portType).The test-suite is completely independent and does not require any other gCube package, except than a local gCore installation. The package is composed by a set of classes, sample configuration files and scripts ready to be executed.
|-lib |--org.gcube.informationsystem.collector.testsuite.jar | |-backup.sh |-restore.sh |-shutdown.sh |-connect.sh
Each script allows to test a different service's operation or group of operations logically related. In the following, an explanation of each script and its usage is provided.
Storing new Documents
Storing a new gCube Document
Invoke the AddDocument.sh tester with the following arguments:
addDocument.sh <host> <port> <scope> <ProfileID> <filename> Profile
Storing a new Instance State Document
Invoke the addDocument.sh tester with the following arguments:
addDocument.sh <host> <port> <scope> <StateID> <filename> InstanceState
Storing a new DAIX Resource Document
Invoke the AddDocument.sh tester with the following arguments:
addDAIXDocument.sh <host> <port> <scope> <ProfileID> <filename> <targetCollectionName>
Retrieving Documents
Getting a gCube Document
Invoke the getDocument.sh tester with the following arguments:
getDocumentsTester.sh <host> <port> <scope> gcube://Profiles/<ProfileType> <ProfileID>
Getting an Instance State Document
Invoke the getDocument.sh tester with the following arguments:
getDocument.sh <host> <port> <scope> gcube://Properties <StateID>
Getting an DAIX Resource Document
Invoke the getDocument.sh tester with the following arguments:
getDocument.sh <host> <port> <scope> gcube://<collectionName> <ResourceID>
Managing the XML Storage
Requesting the XML Storage backup
The backup.sh script invokes the Backup operation of the XMLStorageAccess portType and requests an immediate backup of the XML Storage. It has to be executed as follows:
./backup.sh <IS-Collector host> <IS-Collector port> <scope>
Restoring the latest XML Storage backup
The restore.sh script invokes the Restore operation of the XMLStorageAccess portType and requests the restore of the latest backup of the XML Storage available. It has to be executed as follows:
./restore.sh <IS-Collector host> <IS-Collector port> <scope>
Shutting down the XML Storage
The shutdown.sh script invokes the Shutdown operation of the XMLStorageAccess portType and requests the shutdown of any connection with the XML Storage available. This could be helpful to call before to stop the container on the node in order to have a gently shutdown of the instance. It has to be executed as follows:
./shutdown.sh <IS-Collector host> <IS-Collector port> <scope>
Reconnecting the XML Storage
The connect.sh script invokes the Connect operation of the XMLStorageAccess portType and requests to reopen the needed connections to the XML Storage previously closed with a Shutdown call. It has to be executed as follows:
./coonect.sh <IS-Collector host> <IS-Collector port> <scope>