Difference between revisions of "User Security"
Andreaturli (Talk | contribs) |
m (→Security Basics) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Basics of User Security. Digital Certificates, CAs etc. Authorization and Authentication procedures | Basics of User Security. Digital Certificates, CAs etc. Authorization and Authentication procedures | ||
| − | The | + | The D4Science Security model uses [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_key_infrastructure Public Key Infrastructure] (PKI) mechanisms to authenticate identities acting in the infrastructure. |
| − | Each authenticated invocation must be performed using valid credentials issued by a trusted [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Certificate_authority Certification Authority] (CA). | + | Each authenticated invocation must be performed using valid credentials issued by a trusted [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Certificate_authority Certification Authority] (CA). |
== Acquiring a Digital Certificate == | == Acquiring a Digital Certificate == | ||
| − | The standard procedure for acquiring a Digital Certificate from the appropriate accredited Certification Authority is based on | + | The standard procedure for acquiring a Digital Certificate from the appropriate accredited Certification Authority is based on a certain number of steps. |
| − | Authority is a person responsible to identify | + | |
| + | First of all users has to request a CA certificate and to install it on his browser. | ||
| + | CA policy requests that in your institute a Registration Authority (RA) is defined. A Registration Authority is a person responsible to identify user for CA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Second needed step is requesting a local Registration Authority for a digital certificate. The Registration Authority will start a simple procedure and will give an ID to the user. | ||
| + | After receiving this ID, the user can compile his personal data for CA. The ID verifies them. Then user's browser will ask him for a password: this password is used for encrypting the private key before saving it locally. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The browser generates the couple of private-public key and sends the public key to the CA to be signed. Typically in a day the user receives an email from CA with an URL. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To complete the procedure, the user connects with that URL. For this, s/he must use the same browser and the same machine as used to generate the couple private-public key. The browser installs the certificate (i.e. the public key signed by CA), and the user is requested to enter the password to access to the private key. | ||
| + | At this point the certificate plus the private key are saved and encrypted on the configuration files of the user's web browser. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This certificate can be exported on your filesystem as backup. | ||
== Accessing a Community Portal == | == Accessing a Community Portal == | ||
| − | + | D4Science infrastructure is able to provide credentials to user without a personal certificate. These credentials are generated in a transparently way for the user through the D4Science Portal. (http://portal.d4science.research-infrastructures.eu) | |
| + | |||
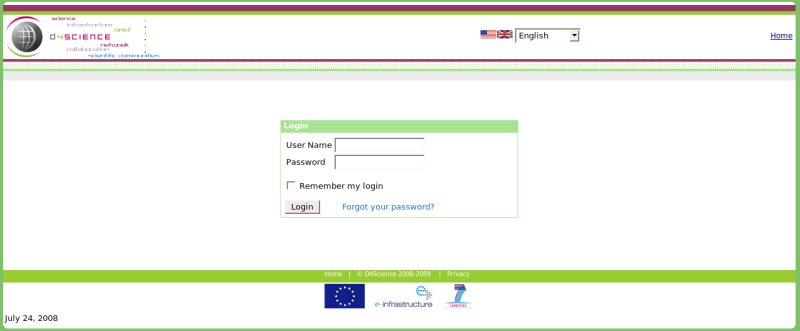
| + | In particular D4Science portal login phase is subdivided in two main steps: | ||
| + | * Insert User Name and Password | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:D4science_login.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * Specify the "VRE to Load". | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:D4science_login_step2.jpg]] | ||
| − | + | This second choice will affect the available credentials for the user during the session. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | In | + | In fact choosing a VRE, the user inherits all the privileges he has in terms of group membership and roles in D4Science VOMS. |
Latest revision as of 19:19, 24 July 2008
Security Basics
Basics of User Security. Digital Certificates, CAs etc. Authorization and Authentication procedures
The D4Science Security model uses Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) mechanisms to authenticate identities acting in the infrastructure.
Each authenticated invocation must be performed using valid credentials issued by a trusted Certification Authority (CA).
Acquiring a Digital Certificate
The standard procedure for acquiring a Digital Certificate from the appropriate accredited Certification Authority is based on a certain number of steps.
First of all users has to request a CA certificate and to install it on his browser. CA policy requests that in your institute a Registration Authority (RA) is defined. A Registration Authority is a person responsible to identify user for CA.
Second needed step is requesting a local Registration Authority for a digital certificate. The Registration Authority will start a simple procedure and will give an ID to the user. After receiving this ID, the user can compile his personal data for CA. The ID verifies them. Then user's browser will ask him for a password: this password is used for encrypting the private key before saving it locally.
The browser generates the couple of private-public key and sends the public key to the CA to be signed. Typically in a day the user receives an email from CA with an URL.
To complete the procedure, the user connects with that URL. For this, s/he must use the same browser and the same machine as used to generate the couple private-public key. The browser installs the certificate (i.e. the public key signed by CA), and the user is requested to enter the password to access to the private key. At this point the certificate plus the private key are saved and encrypted on the configuration files of the user's web browser.
This certificate can be exported on your filesystem as backup.
Accessing a Community Portal
D4Science infrastructure is able to provide credentials to user without a personal certificate. These credentials are generated in a transparently way for the user through the D4Science Portal. (http://portal.d4science.research-infrastructures.eu)
In particular D4Science portal login phase is subdivided in two main steps:
- Insert User Name and Password
- Specify the "VRE to Load".
This second choice will affect the available credentials for the user during the session.
In fact choosing a VRE, the user inherits all the privileges he has in terms of group membership and roles in D4Science VOMS.