Difference between revisions of "Integration Infrastructure"
(Created page with "The tools that take part to the integration of software during a release process are very well integrated each other in order to guarantee an high level of automatism. The sum...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
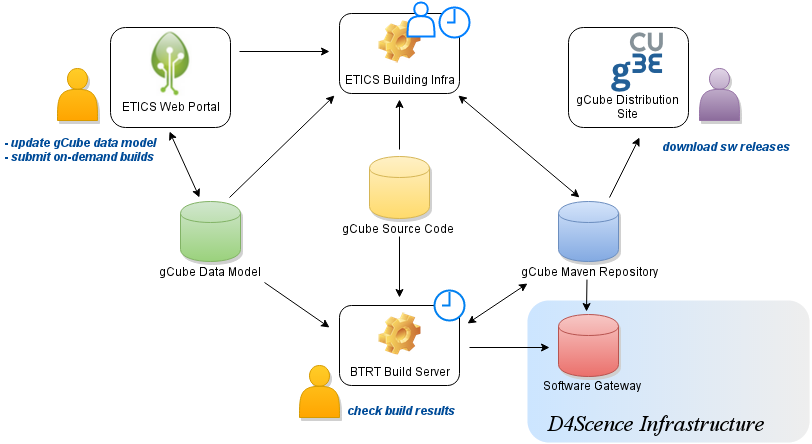
| − | The tools that take part to the integration of software during a release process are very well integrated each other in order to guarantee an high level of automatism. The sum of tools and their interconnections are called ''Integration Infrastructure'' and it is | + | The tools that take part to the integration of software during a release process are very well integrated each other in order to guarantee an high level of automatism. The sum of tools and their interconnections are called ''Integration Infrastructure'' and it is depicted in the figure below. |
[[File:Integration_infrastructure.png|center]] | [[File:Integration_infrastructure.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are three main '''repositories''' in the integration infrastructure: | ||
| + | * the '''gCube Source Code repository''' that contains the source code of all gCube components; | ||
| + | * the '''gCube Data Model repository''' that contains metadata associated to each gCube component related to building and packaging commands, dependencies, project structure (this repository corresponds to the ETICS database); | ||
| + | * the '''gCube Maven repositories''' a set of Maven repositories that hosts all the artifacts produced for each component during the project builds; | ||
| + | |||
| + | A fourth repository, the '''Software Gateway repository''' is considered of interest for the release process. In fact, this repository keeps the list of profiles of all gCube software deployable in a given gCube instance. At the end of the release process, the profile of all components released are pushed in the D4Science Infrastructure Software Gateway in order to make them available for deployment into the production infrastructure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | There four different '''services''' that perform different tasks: | ||
| + | * the '''ETICS Web Portal''' | ||
| + | * the '''ETICS build nodes''' | ||
| + | * '''BTRT''' | ||
| + | * the '''gCube Distribution Site''' | ||
Revision as of 18:29, 7 October 2015
The tools that take part to the integration of software during a release process are very well integrated each other in order to guarantee an high level of automatism. The sum of tools and their interconnections are called Integration Infrastructure and it is depicted in the figure below.
There are three main repositories in the integration infrastructure:
- the gCube Source Code repository that contains the source code of all gCube components;
- the gCube Data Model repository that contains metadata associated to each gCube component related to building and packaging commands, dependencies, project structure (this repository corresponds to the ETICS database);
- the gCube Maven repositories a set of Maven repositories that hosts all the artifacts produced for each component during the project builds;
A fourth repository, the Software Gateway repository is considered of interest for the release process. In fact, this repository keeps the list of profiles of all gCube software deployable in a given gCube instance. At the end of the release process, the profile of all components released are pushed in the D4Science Infrastructure Software Gateway in order to make them available for deployment into the production infrastructure.
There four different services that perform different tasks:
- the ETICS Web Portal
- the ETICS build nodes
- BTRT
- the gCube Distribution Site