IS-Publisher
In conjunction with the IS-Client and the IS-Notification, the IS-Publisher represents the mediation layer gCube Services will rely on to interact with the Information Service as a whole.
Design
The IS-Publisher is a Java library providing a reference implementation for a group of interfaces defined in the gCore Framework. The purpose of these interfaces is to define the behavior of providers of information to the Information System.
More specifically:
- by implementing the
org.gcube.common.core.informationsystem.publisher.ISPublisherinterface, the library allows gCube services to publish GCUBEResources and instances' states as of WS-ResourceProperty documents; - by implementing the
org.gcube.common.core.informationsystem.publisher.ISGenericPublisherandorg.gcube.common.core.informationsystem.publisher.ISResourceinterfaces, the library provides a way to publish generic XML documents in the IS; - by implementing the
org.gcube.common.core.informationsystem.publisher.ISLocalPublisherinterface, it provides a subscription/notification mechanism based on local events.
At runtime, all the above interfaces are dynamically bound by gCore to the implementation provided by the library.
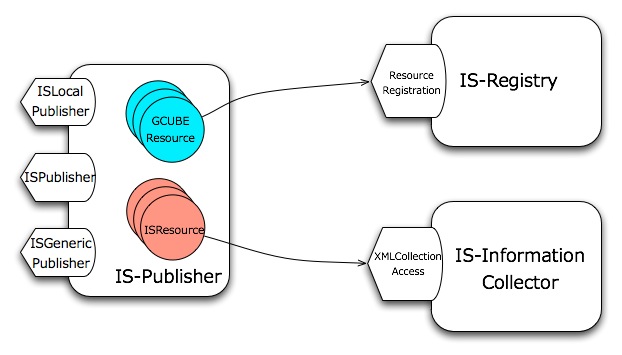
Each registration request creates an internal resource sent to the appropriate IS service. Instance states and generic XML documents are wrapped as ISResources and sent to the Information Collector. GCUBEResources are instead sent to the IS-Registry service for validation and approval.
Managed Resources
Instance State
An instance state is the set stateful WS-Resource created by that instance following the WSRF patterns.
In order to be published, a WS-Resource has to expose a view of its state as a mean of ResourceProperty and declare a registration file for that properties in its JNDI (<service folder>/etc/deploy-jndi-config.xml). This declaration is obtained through the publicationProfile element inside the service section.
This is an example of such declaration:
<service name="..."> <resource name="publicationProfile" type="org.gcube.common.core.state.GCUBEPublicationProfile"> <resourceParams> <parameter> <name>factory</name> <value>org.globus.wsrf.jndi.BeanFactory</value> </parameter> <parameter> <name>mode</name> <value>push</value> </parameter> <parameter> <name>fileName</name> <value>Registration.xml</value> </parameter> </resourceParams> </resource> </service>
The registration file specifies which properties have to be published, when and how following the syntax defined for the WS-MDS Aggregator Source registrations. The following example shows a registration file for 3 resource properties (RPString, RPDate, RPAny):
<ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters xmlns:sgc="http://mds.globus.org/servicegroup/client" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:agg="http://mds.globus.org/aggregator/types" xmlns="http://mds.globus.org/servicegroup/client"> <Content xsi:type="agg:AggregatorContent" xmlns:agg="http://mds.globus.org/aggregator/types"> <agg:AggregatorConfig> <agg:GetMultipleResourcePropertiesPollType xmlns:stateful="http://gcube-system.org/namespaces/test/stateful"> <agg:PollIntervalMillis>60000</agg:PollIntervalMillis> <agg:ResourcePropertyNames>stateful:RPString</agg:ResourcePropertyNames> <agg:ResourcePropertyNames>stateful:RPDate</agg:ResourcePropertyNames> <agg:ResourcePropertyNames>stateful:RPAny</agg:ResourcePropertyNames> </agg:GetMultipleResourcePropertiesPollType> </agg:AggregatorConfig> <agg:AggregatorData/> </Content> </ServiceGroupRegistrationParameters>
Note that the ResourcePropertyNames have to be fully qualified with the namespace declared in the service's WSDL (http//gcube-system.org/namespaces/test/stateful in the example above).
Name of the file aside, the other parameter to consider in the JNDI file is the mode. Clients may select the push or pull to publish their instance state. The chosen mode heavily impacts on the behavior of the ISPublisher.
Publishing with push mode
With the push mode, the resource properties are (re)published whenever the values of one of them changes. If the RPs change every now and then, intermittently or there are peaks of changes in the RPs but longer periods without any change, this is the preferred way to go.
Publishing with pull mode
When RPs change quite frequently and constantly and it's not critical to have them refreshed immediately, the pull mode has to be selected. In this modality, the ISPublisher periodically harvests and collects the RP values from the WS-Resource and publishes them in the Information Collector service.
The polling period is indicated in the PollIntervalMillis parameter inside the registration file.
GCUBEResource
GCUBEResource profiles are managed by interacting with the ResourceRegistration portType of IS-Registry service. The ISPublisher here acts as a simple mediator by selecting the IS-Registry instance in the publishing scope and invoking its operations.
XML Document
Starting from the release 3.0 (Feb 2011), the ISPublisher offers the possibility to publish well-formed XML documents in the IS. This feature exploits the new XMLCollectionAccess portType of the Information Collector compliant with the WS-DAIX specification. This raises significant opportunities for clients to create their own collections of indexed documents that can be queried through the IS-Client library.
Library Implementation Notes
Behind the exposed interfaces, there are three main paths of execution inside the library depending on the type of resources to manage.
If the published resource is a GCUBEResource, it is synchronously sent to the IS-Registry instance in the given scope. The selection of the appropriate instance is done by a set of handlers defined in org.gcube.common.informationsystem.publisher.impl.registrations.resources.
A completely different approach if followed when an Instance State is published. Each registered instance state requires a dedicated running task that reacts to the state changes. An instance of the org.gcube.common.informationsystem.publisher.impl.instancestates.InstanceStatePublisher class keeps track of the activated tasks. If the pull mode has been selected, an instance of RegisterInstanceStatePullHandler class periodically harvests the resource properties document and creates an ISResource to send to the InformationCollector for indexing. If the push mode has been chosen, an instance of RegisterInstanceStatePushHandler acts as an observer of the resource properties values and each time one of them changes receives a notification from the RPSet (gCore) and then sends the resource properties document to the InformationCollector.
The third path is related to the publication of generic XML Documents. The received documents (wrapped as ISResource) are simply sent to the InformationCollector for indexing.
Configuration
The behavior of the ISPublisher can be partially configured via a properties file. This file is located in $GLOBUS_LOCATION/config/ISPublisher.properties. This is an example of such a file with a bit of explanation on the configurable properties:
# Timeout in the communications with the IS-Registry REGISTRY_CHANNEL_TIMEOUT=60000 # Timeout in the communications with the IS-InformationCollector COLLECTOR_CHANNEL_TIMEOUT=120000 # Max number of parallel registrations for this gHN MAX_PARALLEL_REGISTRATIONS=100 # Max tries for publishing the resource (-1 means unlimited attempts) RESOURCE_PUBLICATION_MAX_ATTEMPTS=3 # Interval between two bulk publications BULK_PUBLICATIONS_INTERVAL=20000
Bulked Publications
To support an optimization of the load at infrastructure level, from release 3.0 on, instance states and XML documents to be sent to the InformationCollector are queued and periodically sent in a bulk way (i.e. in a single invocation). This is achieved with a new internal publisher named GCUBEGenericBulkPublisher. The interval between two bulk publications is specified in the BULK_PUBLICATIONS_INTERVAL of the configuration file.