Facet Based Resource Model
Disclaimer
This Model is part of research conducted in the context of a PhD. This wiki page represents just a partial view of the full rationale of the research. To have a complete overview of the rationale of the model, please refer to the PhD thesis which is publicly available at:
https://etd.adm.unipi.it/t/etd-05102019-114151/
https://openportal.isti.cnr.it/doc?id=people______::470484e51fcb9e307a418c800efc44c8
If you need to refer to such work you can cite the PhD Thesis.
BibText:
@phdthesis{frosini2019transactional,
title={Transactional REST Information System for Federated Research Infrastructures enabling Virtual Research Environments},
author={Frosini, Luca},
year={2019},
school={UNIVERSIT{\`A} DI PISA}
}
An previous paper about this work is:
BibText:
@article{frosini2018facet,
title={A Facet-based Open and Extensible Resource Model for Research Data Infrastructures.},
author={Frosini, Luca and Pagano, Pasquale},
journal={Grey Journal (TGJ)},
volume={14},
number={2},
year={2018}
}
IS Model
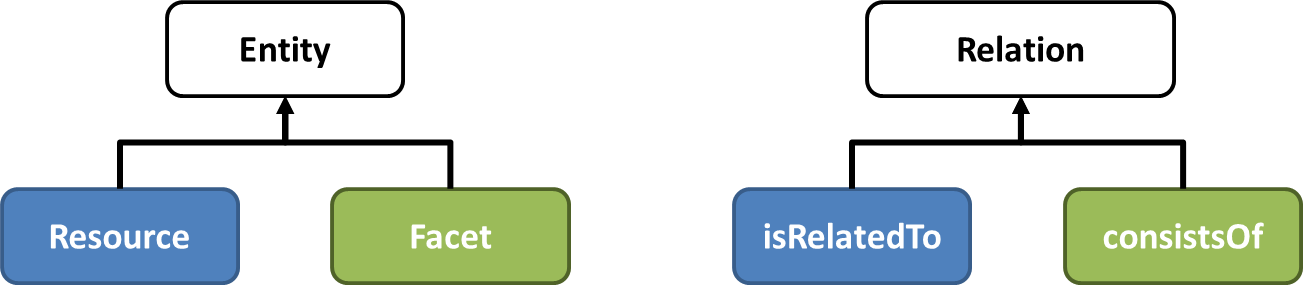
The Information System Model (henceforth IS Model) is a graph model with Entities as nodes and Relations as edges.
IS Model is used by Information System Resource Registry
- Two typologies of entities are envisaged:
- Resources, i.e. entities representing a description of "thing" to be managed;
- Every Resource is described by a number of Facets.
- Facets, i.e. entities contributing to "build" a description of a Resource. Every facet, once attached to a Resource profile captures a certain aspect / characterization of the resource;
- Every facet is characterised by a number of properties;
- Resources, i.e. entities representing a description of "thing" to be managed;
- Two typologies of relations are envisaged:
- isRelatedTo, i.e. a relation linking any two Resources.
- ConsistsOf, i.e. a relation connecting each Resource with one of the Facets characterizing it;
- Each entity and relation
- has an header automatically generated for the sake of identification and provenance of the specific information;
- can be specialized
- A number of specializations are identified below. Such specializations are managed by the gCube Core services, i.e. Core services builds upon these specializations to realize its management tasks;
- Other specializations can be defined by clients, the system make it possible to store these additional typologies of relations and facets and to discover them.
- Facet and Relation instances can have additional properties which are not defined in the schema (henceforth schema-mixed mode).
- On relations:
- Any relation has a direction, i.e. a "source" (out bound of the relation) and a "target" (in bound of the relation). Anyway, the relation can be also navigated in the opposite direction;
- It is not permitted to define a Relation having a Facet as "source". In other words:
- It is not permitted to define a Relation connecting a Facet with another one;
- It is not permitted to define a Relation connecting a Facet with a Resource (as target);
- A Facet instance can be linked (by ConsistsOf or any specialization of it) from different Resources.
We derived the term Facet directly from the dictionary definition. Merriam Webster Dictionary defines facet as “any of the definable aspects that make up a subject (as of contemplation) or an object (as of consideration)”[1]. The Free Dictionary defines a facet as “One of numerous aspects, as of a subject” [2].
Properties
Any Property defined in the schema is characterised by:
- Name : Property Name
- Type : The Type of the Property (e.g. String, Integer, ...). It can be a Basic Type or a Derived Type or a Complex Type
- Description : The description of the Property.
default=null. - Mandatory (M): Indicate if the Property is mandatory.
default=false. - ReadOnly (RO): The Property cannot change its value.
default=false. - NotNull (NN): Whether the property must assume a value diverse from 'null' or not.
default=false - Max (Max):
default=null - Min (Min):
default=null - Regex (Reg)): A Regular Expression to validate the property value,
default=null. A good online tool for regex is avalable at https://regex101.com/
Basic Types
| Type | Java type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Boolean | java.lang.Boolean or boolean
|
Handles only the values True or False. |
| Integer | java.lang.Integer or int or java.math.BigInteger
|
32-bit signed Integers. |
| Short | java.lang.Short or short
|
Small 16-bit signed integers. |
| Long | java.lang.Long or long
|
Big 64-bit signed integers. |
| Float | java.lang.Float or float
|
Decimal numbers. |
| Double | java.lang.Double or double
|
Decimal numbers with high precision. |
| Date | java.util.Date
|
Any date with the precision up to milliseconds. |
| String | java.lang.String
|
Any string as alphanumeric sequence of chars. |
| Property | ? extends org.gcube.informationsystem.model.reference.properties.Property
|
This is an Object contained inside the owner Entity and has no Header. It is reachable only by navigating the owner Entity. |
| |
List<? extends org.gcube.informationsystem.model.reference.properties.Property> |
|
| |
Set<? org.gcube.informationsystem.model.reference.properties.Property> |
|
| Property map | Map<String, ? extends org.gcube.informationsystem.model.reference.properties.Propertyd>
|
Map of Objects contained inside the owner Entity and have no Header. They are reachable only by navigating the owner Entity. |
| Byte | java.lang.Byte or byte
|
Single byte. useful to store small 8-bit signed integers. |
| Binary | java.lang.Byte[] or byte[]
|
Can contain any value as byte array. |
Derived Types
The following are obtained using a String as real type and adding a validation regex.
| Type | Java type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enum | java.lang.Enum or enum
|
by default it is represented using the String representation of the Enum. So that the primitive type used will be String. The enumeration is checked by setting Regexpr property. The Regular Expression is auto-generated and it will be something like ^(FIRST-ENUM-STRING_REPRESENTATION|SECOND-ENUM-STRING_REPRESENTATION|...|LAST_ENUM_STRING_REPRESENTATION)$.
Otherwise (if indicated using an annotation), it can be represented using the Integer value of the Enum. So that the primitive type used will be Integer. The enumeration is checked using |
| UUID | java.util.UUID
|
String representation of the UUID. The check is obtained using the regular expression ^([a-fA-F0-9]{8}-[a-fA-F0-9]{4}-[a-fA-F0-9]{4}-[a-fA-F0-9]{4}-[a-fA-F0-9]{12}){1}$
|
| URL | java.net.URL
|
String representation of the URL. No check actually. |
| URI | java.net.URI
|
String representation of the URI. No check actually. |
| TypeVersion | org.gcube.informationsystem.utils.TypeVersion
|
A type representing and validating a version in the following format X.X.X Major(Integer).Minor(Integer).Revision(Integer) (e.g 1.0.0, 2.3.0, 2.0.1). The check is obtained using the regular expression ^[1-9][0-9]{0,}\.(0|([1-9][0-9]{0,}))\.(0|([1-9][0-9]{0,}))$.
|
Complex Types
Any property defined by composing basic types derives from Property type.
Property
It does not define any field. It is just used as a base class.
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
Header
Every Entity and Relation has an Header automatically created/updated by the System.
| Name | Type | Attributes | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| uuid | UUID | Mandatory=true NotNull=true ReadOnly=true
|
This UUID is be used to identify the Entity or the Relation univocally. |
| creator | String | Mandatory=true NotNull=true ReadOnly=true
|
The user that created the Entity or the Relation. It is initialized at creation time. |
| modifiedBy | String | Mandatory=true NotNull=true
|
The user that made the last update to the Entity or the Relation. At creation time, it assumes the same value of creator. |
| creationTime | Date | Mandatory=true NotNull=true ReadOnly=true
|
Creation time. It represents the difference, measured in milliseconds, between the creation time and midnight, January 1, 1970, UTC. |
| lastUpdateTime | Date | Mandatory=true NotNull=true
|
Last Update time. At creation time it assumes the same value of creationTime. It represents the difference, measured in milliseconds, between the creation time and midnight, January 1, 1970, UTC. |
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
PropagationConstraint
At any time entities and relations can be added or removed to/from a context or deleted. The PropagationConstraint property contained in each relation is a predefined Property type which indicates the behaviour to be held on a target entity when an event related to a context occurs in the source resource or directly to the relation.
| Name | Type | Attributes | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| remove | Enum | Regex=(cascadeWhenOrphan|cascade|keep)
|
It indicates the behaviour to implement for the target Entity when a 'remove' action is performed on the source Resource. Remove actions are: (i) the operation of removing an instance from a context; (ii) the operation of deleting an instance (it has an impact on all contexts). |
| add | Enum | Regex=(propagate|unpropagate)
|
It indicates the behaviour to implement for the target Entity when an 'add' action is performed on the source Resource. Add action is the operation of adding an instance to a context. |
Remove values;
- cascadeWhenOrphan: When a remove action is performed on the source Entity of the relation, or directly on the relation, then the same remove action apart on the relation is performed to the target entity if it has no other incoming relations.
- cascade: When a remove action is performed on the source Entity of the relation, or directly on the relation, then the same remove action is performed on the relation and its target entity.
- keep: When a remove action is performed on the source Entity of the relation, or directly on the relation, then the same remove action is performed on relation but never to the target entity.
Add values;
- propagate: When an 'add' action is performed on the source Entity of the relation, or directly on the relation, then the same add action is performed on the relation and its target Entity.
- unpropagate: When an 'add' action is performed on the source Entity of the relation, is performed on source relation only. Trying to perform an 'add' action on the relation has no effects.
Any Relation contains such a property. If the values are not specified at creation time the system initialize it with the following rules:
- ConsistsOf Relation :
remove=cascadeWhenOrphan,add=propagate - IsRelatedTo Relation :
remove=keep,add=unpropagate
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
Encrypted
| Name | Type | Attributes | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | String | The encrypted value. The resource registry store safely the value. When received the value is decrypted using the key of current context and store the value safely. When the value is read, the resource-registry retrieve the value and encrypt it with the key of current context. |
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
Entity
| Goal: This is the base type for any entity. | ||||
| Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Type | Attributes | Description | |
| header | Header | Mandatory=true NotNull=true ReadOnly=true
|
A distinguishing string to be used by clients to identify the access point of interest. | |
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
Resource
| Scope: This entity is conceived to describe every "main thing" to be registered and discovered by the Information System. | ||||
| Source | Relation | Multiplicity | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Facets | ||||
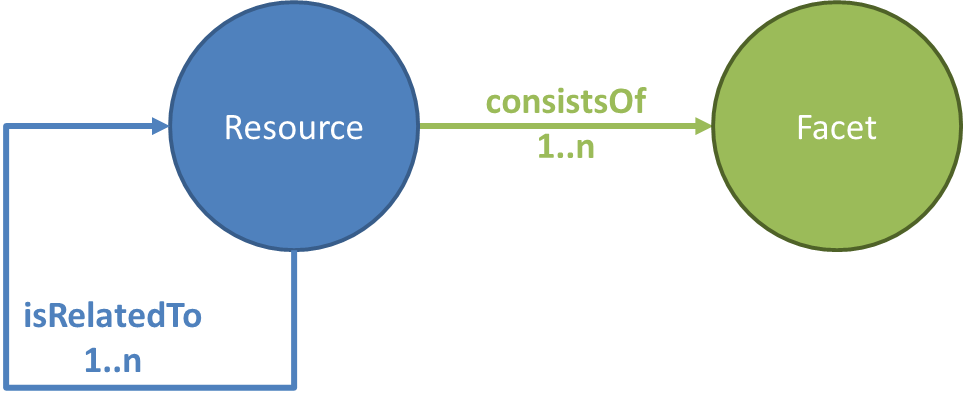
| Resource | ConsistsOf | 1..n | Facet | Any Resource consists of one or more Facets that describes the different aspects of the resource. |
| Relations | ||||
| Resource | isRelatedTo | 0..n | Resource | Any Resource can be related to any other resource. |
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
Facet
Facets are collections of attributes conceived to capture a certain feature/aspect of the Resource they are associated with. Every facet can define zero or more properties. Besides the per-facet envisaged properties, clients can add new ones.
| Goal: This is the base type for any Facet. | ||||
| Known Usage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Relation | Multiplicity | Target | Description |
| Resource | ConsistsOf | 1..n | Facet | Any Resource consist of one or more Facets which describes the different aspects of the resource. |
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
Relation
Every relation has:
- An Header
- A PropagationConstraint
- Zero or More properties (not necessarily predefined, similarly to Facets).
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
IsRelatedTo
| Source | Relation | Multiplicity | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource | IsRelatedTo | 0..n | Resource | A relation linking any two Resources. |
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
ConsistsOf
| Source | Relation | Multiplicity | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource | ConsistsOf | 1..n | Facet | A relation connecting each Resource with one of the Facet characterizing it. |
The Java Interface declaration for such a type is available at:
Internal Entity and Relation
For internal use only are defined the following entity and relation:
Context
Model a Context (aka scope) in the same Application Domain.
| Goal: Models a Context (aka scope). | ||||
| Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Type | Attributes | Description | |
| name | String | Mandatory=true NotNull=true
|
The name of the context. Two Context with the same name can exist but they cannot have the same parent. In other words, a Context cannot have two children with the same name. | |
| Known Usage | ||||
| Source | Relation | Multiplicity | Target | Description |
| Context | isParentOf | 0..n | Context | ... |
isParentOf
This relation has no propagation constraint.
| Source | Relation | Multiplicity | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Context | isParentOf | 0..n | Context | ... |
Best practices and guidelines
- On Facet instances "reuse" across Resource Profiles:
- This can be guaranteed automatically by the system, if and just in the case the system wants to avoid duplication of information. It is based on a configuration policy;
- This MUST be done only when a change in a facet instance MUST affect a change in all Resources connected to such a Facet.