Accounting
GCube Accounting allows to collect information of the infrastructure usage and expose them for the interested consumer.
Contents
Architecture
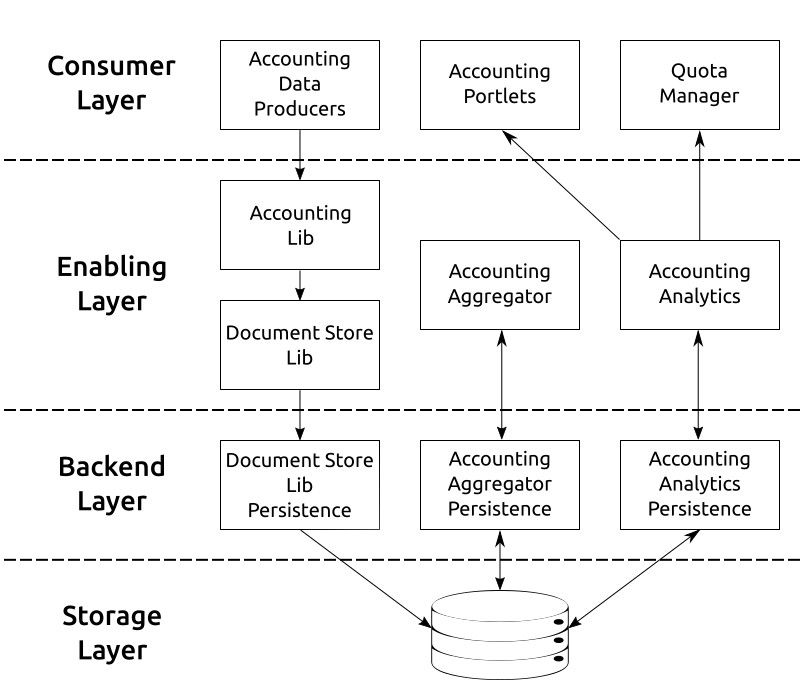
The following picture shows the gCube Accounting architeture
The Accounting Architecture has been logically divided in three different layers.
Moreover we have the storage layer which is not a gCube component in terms of development.
All the developed component must respect this architecture. In particular, the design and the implementation has to respect the following rules:
- Each enabling layer has its own correspondent backend implementation.
- Each backend implementation must be dynamically discovered at runtime. This allow to decouple the deployment of a different backend from the development of the enabling layer. In other word each component on the enabling layer MUST NOT have any dependency over a certain backed implementation.
The only entitled software which can have a dependency against the backend component are the ones that allow to deploy and distribute a consistent infrastructure:
- bundles (e.g. smartgear-bundle, portal-bundle)
- provisioning script
Accounting Enabling Layer
Accounting Storage Layer
This layer is not developed by gCube but the selected technology has to be selected to provide HA (High Availability). Actually CouchDB has been selected as storage for accounting data.
Accounting Backend Layer
- document-store-lib-BACKEND (e.g. document-store-lib-couchdb, document-store-lib-couchbase, document-store-lib-mongodb)
- accounting-analytics-persistence-BACKEND (i.e. accounting-analytics-persistence-couchdb)
- accounting-aggregator-persistence-BACKEND (i.e. accounting-aggregator-persistence-couchdb)
Each component in this layer has been explicitly developed over a certain storage technology. Each component MUST NOT rely on IS to discover the information needed to connect to the underling storage. In other words the component MUST NOT have an hard-cabled connection information or a local configuration files. To retrieve the storage connection information the following parameter must be part of the query:
- underlying storage technology
- enabling component
The first constraint allow to switch to different storage avoiding to switch all nodes together (two underling storage can co-exist). The second allow to keep separated the connection information for each component. This allow to provide create different access policy for different component (e.g. write only for accounting-li-persistence connection and read/write for others, certain HTTP methods for a library and other methods for another).
Accounting Consumer Layer
In this layer we found not only the accounting consumer which retrieve information related to collected data (e.g. Accounting Manager Portlet) but also all the component which collect data and use accounting-lib to persist in a common pattern.