Statistical Algorithms Importer: Linux-compiled Project FAQ
From Gcube Wiki
F.A.Q. of Statistical Algorithms Importer (SAI), here are common mistakes we have found in Linux-compiled Project.
How to use the input and output parameters (C++ Example)
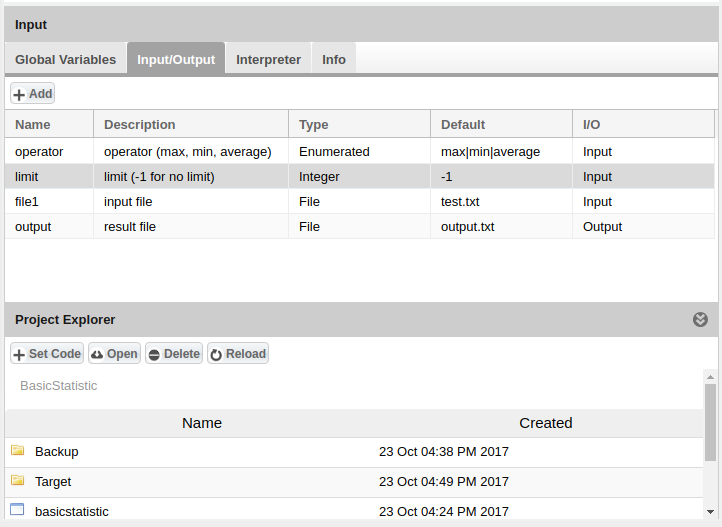
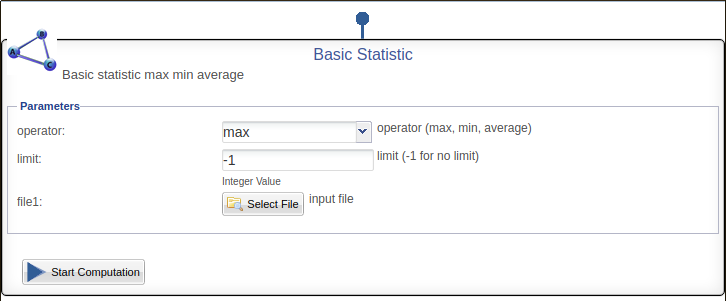
- For example we consider BasicStatistic algorithm that use basicstatistic linux executable file:
- DataMiner show the BasicStatistic algorithm in this way:
- Below the C++ code in sample which generates basicstatistic linux executable file:
//============================================================================ // Name : BasicStatistic.cpp // Author : Giancarlo Panichi // Version : // Copyright : GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE. Version 3.0 // Description : BasicStatistic in C++, Ansi-style //============================================================================ #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char **argv) { printf("BasicStatistic"); printf("Operator: %s\n", argv[1]); printf("Maximum number of items considered: %s\n", argv[2]); printf("Input file: %s\n", argv[3]); FILE * finput; char * line = NULL; size_t len = 0; ssize_t read; finput = fopen(argv[3], "r"); if (finput == NULL) { printf("No input file found: %s\n", argv[3]); return -1; } int limit = atoi(argv[2]); int i = 0; int value = 0; int result = 0; while (((read = getline(&line, &len, finput)) != -1) && (i < limit || limit == -1)) { printf("Retrieved line of length %zu and value: %s", read, line); value = atoi(line); if (i == 0) { result = value; } else { if (strcmp(argv[1], "max") == 0) { if (value > result) { result = value; } } else { if (strcmp(argv[1], "min") == 0) { if (value < result) { result = value; } } else { if (strcmp(argv[1], "average") == 0) { result = result + value; } else { break; } } } } i++; } if (strcmp(argv[1], "average") == 0 && i > 0) { result = result / i; } fclose(finput); if (line) { free(line); } //Write result FILE *foutput = fopen("output.txt", "w"); if (foutput == NULL) { printf("Error opening file!\n"); return -1; } fprintf(foutput, "BasicStatistic Result: \n"); fprintf(foutput, "%d\n", result); fclose(foutput); return 0; }
- test.txt:
9 20 12 23 44 65 80 100
- with basicstatistic max -1 test.txt, output.txt:
BasicStatistic Result: 100
- BasicStatistic code:
Fortran Example
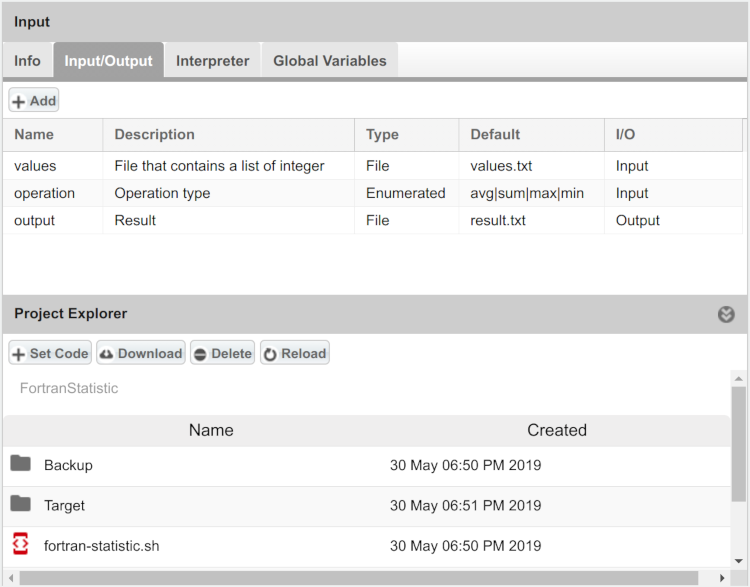
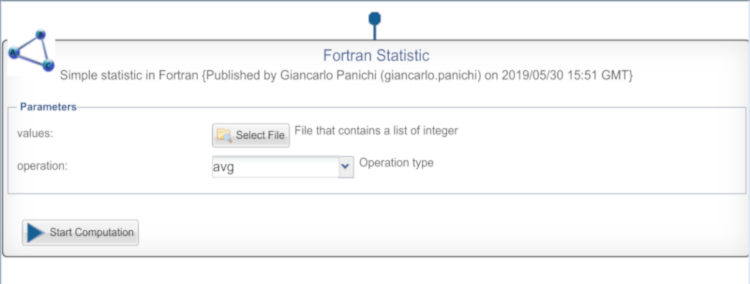
- For example we consider Fortran Statistic algorithm and we will use its executable version fortran-statistic.sh in SAI in this way:
- DataMiner show the Fortran Statistic algorithm in this way:
- values.txt:
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
- with fortranstatistic values.txt avg, result.txt:
The result is: 55
- FortranStatistic code: