GCat Service
gCat Service is a RESTful service enabling any client to programmatically interact with the gCube Catalogue. gCat Service uses the principles defined in gCat Background
Contents
Request
URL
The URL used to interact with gCat is composed of two parts:
- Base Service URL (e.g. https:/gcat.d4science.org/gcat)
- Specific API (e.g. /organizations)
D4Science infrastructure uses cloud facilities allowing to replicate a service to achieve failover and load balancing.
gCat instances can be deployed and undeployed dynamically. For such a reason the Base Service URL MUST NOT be hard-cabled in the code because it can change over time.
To dynamically discover the Base Service URL you can use the Registry RESTful Service
You need to discover gCore Resource having:
- class : DataPublishing
- name : gcat
HTTP Headers
gCube Authorization Token
Any request performed to gCat MUST contains the gCube Authorization Token.
This is done using the HTTP Header gcube-token
gcube-token: YOUR-TOKEN
The gcube-token HTTP header acts as the standard Authorization HTTP header. Plese note that Authorization HTTP header cannot be used in place of gcube-token HTTP header.
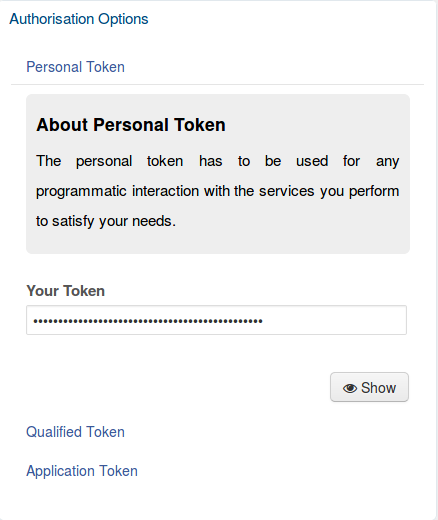
Retrieve your gCube Authorization Token
the gCube Authorization Token is a UUID bound to yourself and a given Infrastructure context. To retrieve it, you just need to go to a VRE for which you are interested and use the Authorisation Options portlet (see below)
Click on Show button and select the token.
Content Type
Any request must contain the indication of the interested content type.
For any operation returning a result, the client must specify the Accept HTTP Header.
Accept: application/json
For any operation sending content to the service, it is necessary to specify the Content-Type HTTP Header.
Content-Type: application/json
Actually, the service accepts and returns only JSON objects.
Except for a profile which can be also requested in XML.
HTTP Statuses
Any successful operation returns 200 OK status code except for create operation which return 201 Created or for the operations which do not provide any content and returns 204 No Content.
The most common error status a client can obtain are
- 400 Bad Request used to indicate a clients error https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.1;
- 401 Unauthorized used to indicate that the client does not provided the gcube-token HTTP Header or the clinet has not enough right to perform such request https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-3.1;
- 404 Not Found used to indicate that the requested instance does not exists https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.4;
- 405 Method Not Allowed the used HTTP method is not supported for the requested URL https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.5.
The response contains the Allow HTTP Header indicating the supported HTTP method for such URL https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.4.1; - 409 Conflict the request could not be completed due to a conflict with the current state of the target resource (e.g. the name of the resource already exists). https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.8.];
- 500 Internal Server Error indicate a server failure. https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.1.
A complete list of HTTP Status can be found here: https://httpstatuses.com/
You can report a 500 Internal Server Error the ticketing system. Please use this checklist before reporting an error:
- replicate the request
- the failure could be temporal due to network error, server issue so please retry the request after a certain amount of time
- indicate how to replicate the error
- indicate the time when the error occurred (this simplify the identification of the issue)
HTTP Methods
To be RESTful compliant gCat uses standard HTTP Methods to perform a listing of collections and CRUD (Create Read Update Delete) operations on instances.
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL | Success HTTP Status | Safe | Idempotent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supported HTTP Methods |
OPTIONS | /{COLLECTION} | 204 No Content (Supported HTTP Methods in Allow HTTP Header) |
Y | Y |
| List | GET | /{COLLECTION} | 200 OK | Y | Y |
| Exists | HEAD | /{COLLECTION} | 204 No Content | Y | Y |
| Create | POST | /{COLLECTION} | 201 Created | N | N |
| Supported HTTP Methods |
OPTIONS | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 204 No Content (Supported HTTP Methods in Allow HTTP Header) |
Y | Y |
| Exist | HEAD | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 204 No Content | Y | Y |
| Read | GET | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 200 OK | Y | Y |
| Update | PUT | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 200 OK | N | Y |
| Patch | PATCH | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 200 OK | N | Y |
| Delete | DELETE | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 204 No Content | N | N ‡ |
| Purge | PURGE | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 204 No Content | N | N ‡ |
| Purge | DELETE | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID}?purge=true | 204 No Content | N | N ‡ |
About URL:
- {COLLECTION} is the plural name of the entity type;
- {INSTANCE_ID} is an identification which enables to univocally identify the instance in the collection.
About Safety and Idempotency properties:
- A method is Safe if it does not produce any side effects. "This does not prevent an implementation from including behaviour that is potentially harmful, that is not entirely read-only, or that causes side effects while invoking a safe method" https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-4.2.1;
- A method is Idempotent if the same operation repeated multiple times has the same side effect than using it one time. "repeating the request will have the same intended effect, even if the original request succeeded, though the response might differ" https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-4.2.2.
‡ DELETE has been defined as idempotent. Allamaraju[1] argues that DELETE idempotency should be accomplished client-side. The server should inform the client if a delete succeeded because the resource was really deleted or it was not found i.e., 404 Not Found error is suggested instead of 204 No Content. The latter situation should be treated as idempotent by the client. For this reason, gCat does not provide server-side idempotency for DELETE and PURGE operations.
You can find more information about HTTP Methods at https://restfulapi.net/http-methods/
Uncommon HTTP Methods:
- PATCH method allows to perform a differential update (i.e. an update which provide only the differences and not the whole new representation) [];
- PURGE method is not a standard but is a widely used in service which requires this action (e.g. Varnish, Squid). gCat provide support for this method but to support a wider range of clients it also provides the Purge action via DELETE with the additional get parameter
purge=true
Collections
Collections available to any users. Non-safe methods can only be invoked by Catalogue Editor
Collections available only for Catalogue Admin
For each collection HEAD and OPTIONS operations are not shown in tables even there are always available.
To keep this documentation simple, for each collection is presented only the relevant attributes of an instance. This allows getting the picture of the content of a request or the content of a response.
Item Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /items?limit=10&offset=0 |
| Create | POST | /items[?social_post=true] |
| Read | GET | /items/{NAME} |
| Update | PUT | /items/{NAME} |
| Delete | DELETE | /items/{NAME} |
| Purge | PURGE | /items/{NAME} |
| Purge | DELETE | /items/{NAME}?purge=true |
The listing API provides paginated results by using the query parameters limit and offset.
To get unlimited results the limit query parameters must be set to -1
An Item is mainly described by the following attributes (* indicate mandatory attributes):
- name* (string): the name of the new item, must be between 2 and 100 characters long and contain only lowercase alphanumeric characters, '-' and '_';
- title (string, defaut="same as name"): the title of the item;
- private* (bool): If True creates a private item;
- maintainer (string): the name of the item’s maintainer;
- maintainer_email (string): the email address of the item’s maintainer;
- license_id* (license id string): the id of the item’s license, see license_list() for available values;
- notes (string): a description of the item;
- url (string): a URL for the item’s source;
- version (string, no longer than 100 characters): ...;
- state (string, default='active'): the current state of the item, e.g. 'active' or 'deleted', only active items show up in search results and other lists of items, this parameter will be ignored if you are not authorized to change the state of the item;
- groups (list of dictionaries): the groups to which the item belongs, each group dictionary should have one or more of the following keys which identify an existing group: 'id' (the id of the group, string), or 'name' (the name of the group, string). To see which groups exist use list method in Group Collection
- tags (list of tag dictionaries): the item’s tags. The tag is a dictionary in the format:
- name : the name for the tag, a string between 2 and 100 characters long containing only alphanumeric characters and '-, '_' and '.'.
- resources (list of resource dictionaries): the item’s resources, see Resource Collection for the format of resource dictionaries;
- extras (list of item extra dictionaries): the item’s extras, extras are arbitrary (key: value) metadata items that can be added to items, each extra dictionary should have keys 'key' (a string), 'value' (a string).
Parameter automatically managed:
- author (string): the name of the item’s author (the owner of the gcube-token);
- author_email (string): the email address of the item’s author (the email of the owner of gcube-token);
- owner_org (string): the id of the item’s owning organization, see organization_list() or organization_list_for_user() for available values (the VRE corrsponding to the gcube-token).
If at least one profile has been defined within this context, then you need to specify the profile's type when creating the item. You need to insert, among the extras of the JSON object describing the item, a system:type property with the proper value (i.e. its value must be equal to the type property contained in the profile). The validation of the submitted request will be performed against the profile whose type has been specified. The other profile's properties need to be specified within extras field as well.
If no profile has been defined, then no validation will be performed. Thus you do not need to set any system:type property.
Suppose you discover that in the context you are willing to publish are defined the following profiles: 'A', 'B' and 'C'.
You are interested in publishing an item with profile 'A', thus you download the XML of profile 'A' which looks like the following
<metadataformat type="Type A"> <metadatafield categoryref="category1"> <fieldName>Field 1</fieldName> <mandatory>false</mandatory> <dataType>String</dataType> <defaultValue /> <note>Write something here</note> <validator /> <tagging create="true" separator="-">onFieldName</tagging> </metadatafield> <metadatafield categoryref="category1"> <fieldName>Field 2</fieldName> <mandatory>false</mandatory> <dataType>Boolean</dataType> <defaultValue>true</defaultValue> <note>Set true or false to the checkbox</note> <validator /> </metadatafield> <metadatafield categoryref="category2"> <fieldName>Field 3</fieldName> <mandatory>true</mandatory> <dataType>String</dataType> <defaultValue>A</defaultValue> <note>A listbox of values</note> <vocabulary isMultiSelection="true"> <vocabularyField>A3</vocabularyField> <vocabularyField>B3</vocabularyField> <vocabularyField>C3</vocabularyField> <vocabularyField>D3</vocabularyField> <vocabularyField>E3</vocabularyField> <vocabularyField>F3</vocabularyField> </vocabulary> <validator /> <tagging create="true" separator="-">onValue</tagging> </metadatafield> <metadatafield categoryref="category2"> <fieldName>Field 4</fieldName> <mandatory>true</mandatory> <dataType>Number</dataType> <defaultValue>4</defaultValue> <validator /> </metadatafield> </metadataformat>
The previous information can be easily discovered with the Profile Collection. Then, the JSON object of the create request will look like
{
"name":"my-item-type-a",
"title":"My Item with Type A",
"private": false,
"license_id":"cc-by",
"tags":[
{
"name":"my-tag"
},
....
],
"groups":[
{
"name":"group-1"
},
....
],
"extras":[
{
"key":"system:type",
"value":"Type A"
},
{
"key":"category1:Field 1",
"value":"Field 1 value"
},
{
"key":"category2:Field 3",
"value":"A3"
},
{
"key":"category2:Field 3",
"value":"F3"
},
{
"key":"category2:Field 4",
"value":"5"
}
]
}
Resource Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /items/{ITEM_ID}/resources |
| Create | POST | /items/{ITEM_ID}/resources |
| Read | GET | /items/{ITEM_ID}/resources/{ID} |
| Update | PUT | /items/{ITEM_ID}/resources/{ID} |
| Delete | DELETE | /items/{ITEM_ID}/resources/{ID} |
An Resource is mainly described by the following attributes (* indicate mandatory attributes):
- name* (string);
- url* (string): url of resource;
-
package_id* (string): id of the item that the resource should be added to; - revision_id (string);
- description (string);
- format (string);
- mimetype (string);
- created (iso date string);
- last_modified (iso date string);
Profile Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /profiles |
| Create | PUT | /profiles/{NAME} |
| Read | GET | /profiles/{NAME} |
| Update | PUT | /profiles/{NAME} |
| Delete | DELETE | /profiles/{NAME} |
Only a Catalogue Admin can manipulate profiles (Create, Update, Delete). These operation are available starting from gCat 1.1.0.
At creation and update time the provided profile is validated against the defined XSD schema (see Item Profile Defintion v3)
A profile is defined using XML. In place of application/json Use
Accept : application/xml
and
Content-Type : application/xml
Listing return a JSON Array. It is also possible to read the representation of a profile as JSON which is an automatic mapping to of the original XML definition to JSON.
An example of Profiles listing is :
[
"EOSCService",
"SoBigData.eu: Dataset Metadata",
"SoBigData.eu: Application Metadata",
"SoBigData.eu: Method Metadata"
]
An example of Profile is :
<metadataformat type="SoBigData Method"> <metadatafield> <fieldName>External Identifier</fieldName> <dataType>String</dataType> <mandatory>false</mandatory> <note>This applies only to methods that have been already published. Insert here a DOI, an handle, and any other Identifier assigned when publishing the dataset alsewhere.</note> </metadatafield> <metadatafield> <fieldName>Creator</fieldName> <mandatory>true</mandatory> <note>The name of the creator, with email and ORCID. The format should be: family, given[, email][, ORCID]. Example: Smith, John, js@acme.org, orcid.org//0000-0002-1825-0097</note> <validator> <regularExpression>^[a-zA-Z .'-]+, [a-zA-Z .'-]+[, ]*([a-zA-Z0-9_!#$%’*+=?`{|}~^.-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+)?[, ]*(orcid.org\/\/0000-000(1-[5-9]|2-[0-9]|3-[0-4])\d\d\d-\d\d\d[\dX])?$</regularExpression> </validator> </metadatafield> <metadatafield> <fieldName>CreationDate</fieldName> <mandatory>true</mandatory> <dataType>Time</dataType> <note>The date of creation of the dataset (different from the date of registration of the dataset automatically added by the system). Use ISO 8601 Date Format: YYYY-MM-DD[ HH:MM] Ex. 1998-11-10 or 2015-05-29 11:55</note> <validator> <regularExpression>^(\d{4}\-(0?[1-9]|1[012])\-(0?[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))+([ ]+(\d{2}(:?\d{2})?)?)?$</regularExpression> </validator> </metadatafield> <metadatafield> <fieldName>Owner</fieldName> <mandatory>true</mandatory> <note>The name of the owner, with email and ORCID. The format should be: family, given[, email][, ORCID]. Example: Smith, John, js@acme.org, orcid.org//0000-0002-1825-0097</note> <validator> <regularExpression>^[a-zA-Z .'-]+, [a-zA-Z .'-]+[, ]*([a-zA-Z0-9_!#$%’*+=?`{|}~^.-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+)?[, ]*(orcid.org\/\/0000-000(1-[5-9]|2-[0-9]|3-[0-4])\d\d\d-\d\d\d[\dX])?$</regularExpression> </validator> </metadatafield> .... <metadatafield> <fieldName>License term</fieldName> <mandatory>false</mandatory> <dataType>Time_Interval</dataType> <note>Period of time during which the dataset may be used. Use ISO 8601 Date Format: YYYY-MM-DD[ HH:MM] Ex. 2016-07-31 or 2015-05-10 12:00</note> <vocabulary/> <validator> <regularExpression>^(\d{4}\-(0?[1-9]|1[012])\-(0?[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))+([ ]+(\d{2}(:?\d{2})?)?)?$</regularExpression> </validator> </metadatafield> <metadatafield> <fieldName>Requirement of non-disclosure (confidentiality mark)</fieldName> <mandatory>false</mandatory> <note>Requirement of non-disclosure (confidentiality mark). Whether the dataset bears confidentiality mark/may be used and shared subject to the obligation of non-disclosure</note> </metadatafield> </metadataformat>
You can find all details about profiles at Item Profile
Namespace Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /namespaces |
An example of given result is:
[
{
"id": "contact",
"title": "Contact Title",
"name": "contact",
"description": "This section is about Contact(s)"
},
{
"id": "developer_information",
"title": "Developer Information",
"name": "developer_information",
"description": "This section is about Developer(s)"
},
{
"id": "extra_information",
"title": "Extras",
"name": "extra_information",
"description": "This section is about Extra(s)"
},
{
"id": "ReportDetails",
"title": "Report Details",
"name": "ReportDetails",
"description": "Report Details"
}
]
License Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /licenses |
An example of given result is:
[
{
"status": "active",
"maintainer": "Creative Commons",
"od_conformance": "rejected",
"family": "Creative Commons",
"osd_conformance": "not reviewed",
"domain_data": true,
"title": "Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0",
"url": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/",
"domain_content": true,
"is_okd_compliant": false,
"is_osi_compliant": false,
"domain_software": false,
"id": "CC-BY-NC-SA-4.0"
},
{
"status": "active",
"maintainer": "Creative Commons",
"od_conformance": "rejected",
"family": "Creative Commons",
"osd_conformance": "not reviewed",
"domain_data": true,
"title": "Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0",
"url": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"domain_content": true,
"is_okd_compliant": false,
"is_osi_compliant": false,
"domain_software": false,
"id": "CC-BY-NC-ND-4.0"
},
...
{
"status": "active",
"maintainer": "Free Software Foundation",
"od_conformance": "not reviewed",
"family": "",
"osd_conformance": "approved",
"domain_data": false,
"title": "GNU Affero General Public License v3",
"url": "http://www.opensource.org/licenses/AGPL-3.0",
"domain_content": false,
"is_okd_compliant": false,
"is_osi_compliant": true,
"domain_software": true,
"id": "AGPL-3.0"
}
]
Group Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /groups |
| Create | POST | /groups |
| Read | GET | /groups/{NAME} |
| Update | PUT | /groups/{NAME} |
| Patch | PATCH | /groups/{NAME} |
| Delete | DELETE | /groups/{NAME} |
| Purge | PURGE | /groups/{NAME} |
| Purge | DELETE | /groups/{NAME}?purge=true |
Only Catalogue Admin are able to invoke non-safe methods.
A group is mainly described by the following attributes (* indicate mandatory attributes):
- name* (string): the name of the group, a string between 2 and 100 characters long, containing only lowercase alphanumeric characters, '-' and '_' ;
- id (string): the id of the group;
- title (string): the title of the group;
- description (string): the description of the group;
- image_url (string): the URL to an image to be displayed on the group’s page;
- state (string, default: 'active'): the current state of the group, e.g. 'active' or 'deleted', only active groups show up in search results and other lists of groups, this parameter will be ignored if you are not authorized to change the state of the group;
- extras (list of dataset extra dictionaries): the group’s extras, extras are arbitrary (key: value) metadata items that can be added to groups, each extra dictionary should have keys 'key' (a string), 'value' (a string), and optionally 'deleted'.
Representation
An example of Group representation is:
{
"name": "group_name",
"id": "fd72502e-ddfa-4121-a12a-bb42e572d649",
"title": "Group Title",
"description": "",
"image_url": "",
"state": "active",
"extras": [],
"created": "2018-03-22T11:48:42.612063",
"revision_id": "0b5dda21-9bb0-4993-896b-d865e0d2f1f3"
}
Organization Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /organizations |
| Create | POST | /organizations |
| Read | GET | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Update | PUT | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Patch | PATCH | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Delete | DELETE | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Purge | PURGE | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Purge | DELETE | /organizations/{NAME}?purge=true |
Only Catalogue Admin are able to invoke non-safe methods.
An Organization is mainly described by the following attributes (* indicate mandatory attributes):
- name* (string): the name of the organization, a string between 2 and 100 characters long, containing only lowercase alphanumeric characters, '-' and '_';
- id (string): the id of the organization;
- title (string): the title of the organization;
- description (string): the description of the organization;
- image_url (string): the URL to an image to be displayed on the organization’s page;
- state (string, default: 'active'): the current state of the organization, e.g. 'active' or 'deleted', only active organizations show up in search results and other lists of organizations, this parameter will be ignored if you are not authorized to change the state of the organization;
- approval_status (string);
- extras (list of dataset extra dictionaries): the organization’s extras (optional), extras are arbitrary (key: value) metadata items that can be added to organizations, each extra dictionary should have keys 'key' (a string), 'value' (a string), and optionally 'deleted'.
User Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /users |
| Create | POST | /users |
| Read | GET | /users/{NAME} |
| Update | PUT | /users/{NAME} |
| Delete | DELETE | /users/{NAME} |
Only Catalogue Admin are able to invoke non-safe methods.
A User is mainly described by the following attributes (* indicate mandatory attributes):
- name* (string): the name of the user, a string between 2 and 100 characters in length, containing only lowercase alphanumeric characters, '-' and '_';
- id (string): the id of the user;
- fullname (string): the full name of the user;
- email (string): the email address for the user;
- password (string): the password of the user, a string of at least 4 characters (parameter only used to create a new user);
- about (string): a description of the user.
{
"name": "luca_frosini",
"id": " 5f5c2bc0-bcd4-460a-9548-52cd4d33b263",
"fullname": "Luca Frosini"
}
- ↑ Allamaraju S. RESTful Web Services Cookbook: Solutions for Improving Scalability and Simplicity . O’Reilly. first ed. 2010