Difference between revisions of "SDI Overview"
(→Third party service registration) |
(→Administration) |
||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
== Administration == | == Administration == | ||
In this section we describe the most commonly relevant information in managing gCube SDI. | In this section we describe the most commonly relevant information in managing gCube SDI. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:SDI_Service_Architecture.png|frame|center|SDI Architecture]] | ||
=== Third party service registration === | === Third party service registration === | ||
| Line 83: | Line 85: | ||
'''NB''' : SDI Service allows for the proper creation of a Service Endpoint via its HTTP API methods. This method might be usefully integrated with provisioning tasks. More information at [[https://wiki.gcube-system.org/gcube/Interaction_with_SDI-Service#REST_Interface | SDI Service REST Interface]] | '''NB''' : SDI Service allows for the proper creation of a Service Endpoint via its HTTP API methods. This method might be usefully integrated with provisioning tasks. More information at [[https://wiki.gcube-system.org/gcube/Interaction_with_SDI-Service#REST_Interface | SDI Service REST Interface]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Additional IS Resources === | ||
| + | In the following use cases, additional IS Resources are needed in the gCube context of interest: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Metadata publication via gis-interface / geonetwork library : see [[ServiceManager_Guide#Metadata_Publication]] | ||
| + | * Postgis data publication : The user is expected to declare the DB expected resource coordinates (e.g. see [[ServiceManager_Guide#SDI_Indexer]]). Please note that the DB needs to be configured in Geoserver (via GeoServer API or via its GUI). | ||
=== Information === | === Information === | ||
| + | In this section we describe specific aspects related to Third party service provisioning : | ||
| + | |||
| + | * GeoNetwork : currently it needs a postgres DB for its users. In case a postgis connection i provided, it is also used a spatial index. | ||
| + | * GeoServer : It needs at least a DB for its users. Additional postgres DBs are optional, since it supports other data formats relying to the local file system (location /srv/geoserver_data) | ||
| + | * Thredds : It only uses local file system for its data. Configuration relies on local xml files. | ||
| + | |||
=== Tools === | === Tools === | ||
| + | Administration and monitoring utilities are reported here : | ||
| + | |||
| + | * SDI Service : | ||
| + | ** Current SDI Configuration : [[this]] API method can be used to easily retrieve/check current SDI configuration in a context, including instances, credentials and specific details. | ||
| + | ** SDI Health Status : [[this]] API method provides a report on current configuration problems in a specific gCube Context. The report is in XML form thus can be easily programmatically exploited for Infrastructure monitoring. | ||
Revision as of 17:37, 13 March 2023
This page aims to provide an overview of gCube Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) facilities for gCube developers and administrators.
Contents
Overview
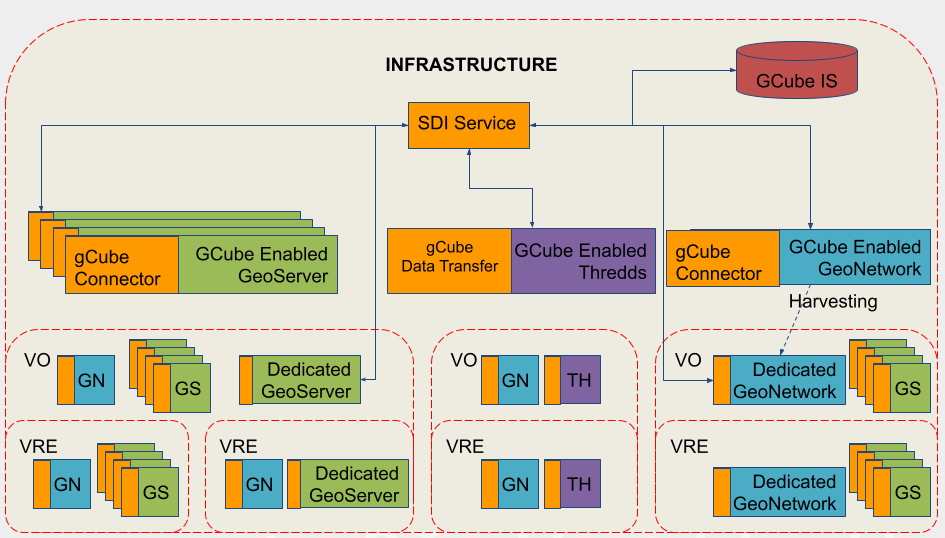
gCube SDI is the set of engines and logic responsible of dealing with 'GIS data management in a gCube Infrastructure.
Third party engines are exploited for their core GIS features (i.e. store/access to GIS data/metadata), while gCube libraries and services orchestrate and integrate these engines in the gCube Infrastructure.
gCube libraries in general provide :
- Context-oriented credential management, in order to enforce access policies to published (meta)
- Metadata enrichment in publication phase
- GIS (meta)data publication utilities
NB : It is important to note that while the use of gCube Logic is recommended, various use cases may directly exploit provided third party engines for various reasons.
Third Party Engines
In gCube SDI, third party engines are exploited for their GIS data/metadata management, more in details we use :
- GeoNetwork :
- Store GIS ISO Metadata (xml)
- Expose metadata with CSW
- Harvest metadata
- GeoServer :
- Store GIS DATA (e.g. shp, postgis, geopackage)
- Expose data with WMS, WFS, WCS..
- Thredds :
- Store GIS DATA
- Expose data with WMS, WFS, WCS..
Managed Credentials
GeoNetwork credentials are managed by gCube org.gcube.spatial.data.geonetwork library and org.gcube.spatial.data.sdi-service SmartGear service. These credentials are generated as needed, and configured in such a way that metadata visibility between gCube contexts reflects gCube policies (more information here).
GeoServer and Thredds credentials are loosely managed, meaning that only administrator user is used in order to publish data to these engines.
gCube Logic
During SDI evolution, distributed gCube logic evolved according to emerging needs while trying to maintain retro-compatibility. For this reason, some components may still be used while being deprecated (e.g. ws-thredds) and there is still some overlap between logic.
Following list aims to provide a generic overview of provided gCube logic features by component :
- org.gcube.spatial.data.geonetwork Library
- Client for GeoNetwork service
- Metadata publication utilities
- Metadata enhancement (NB uses IS Generic Resource, more information at GeoNetwork_library#Metadata_generation_facilities)
- GeoNetwork credentials management (generation and retrieval)
- org.gcube.spatial.data.gis-interface Library
- Data publication utilities with contextual metadata publishing (uses org.gcube.spatial.data.geonetwork for metadata)
- Currently supported data engine is only GeoServer
- org.gcube.spatial.data.sdi-service SmartGear Service
- Credentials management and retrieval
- Metadata enhancement via template application (used in Thredds publication, see ws-thredds below)
- SDI configuration management
- org.gcube.spatial.data.ws-thredds Deprecated Library
- Synchronize a ws-folder with a Thredds catalog, generating and publishing metadata on GeoNetwork
Connectors
These components are library which implement a Web Application Filter in order to :
- Intercept incoming http(s) requests
- If gcube-token is declared, then retrieve credentials from SDI Service and set them in the current request
This allows for authentication within third party engines unaware of gCube logic, by using gcube-token. NB : this approach is considered obsolete and should be changed in favor of oauth integration.
Available connectors are :
- GeoNetwork : org.gcube.data.access.geonetwork.gcube-geonetwork-connector
- GeoServer : org.gcube.data.access.geoserver.gcube-geoserver-connector
Administration
In this section we describe the most commonly relevant information in managing gCube SDI.
Third party service registration
In order to register a third party service in the SDI in a certain context, administrators will need to :
- Properly provision the third party service node in order to work in the context of interest
- Create its related Service Endpoint.
Service Endpoint details vary according to the engine at matter, more information should be available at ServiceManager_Guide.
NB : SDI Service allows for the proper creation of a Service Endpoint via its HTTP API methods. This method might be usefully integrated with provisioning tasks. More information at [| SDI Service REST Interface]
Additional IS Resources
In the following use cases, additional IS Resources are needed in the gCube context of interest:
- Metadata publication via gis-interface / geonetwork library : see ServiceManager_Guide#Metadata_Publication
- Postgis data publication : The user is expected to declare the DB expected resource coordinates (e.g. see ServiceManager_Guide#SDI_Indexer). Please note that the DB needs to be configured in Geoserver (via GeoServer API or via its GUI).
Information
In this section we describe specific aspects related to Third party service provisioning :
- GeoNetwork : currently it needs a postgres DB for its users. In case a postgis connection i provided, it is also used a spatial index.
- GeoServer : It needs at least a DB for its users. Additional postgres DBs are optional, since it supports other data formats relying to the local file system (location /srv/geoserver_data)
- Thredds : It only uses local file system for its data. Configuration relies on local xml files.
Tools
Administration and monitoring utilities are reported here :
- SDI Service :
- Current SDI Configuration : this API method can be used to easily retrieve/check current SDI configuration in a context, including instances, credentials and specific details.
- SDI Health Status : this API method provides a report on current configuration problems in a specific gCube Context. The report is in XML form thus can be easily programmatically exploited for Infrastructure monitoring.