Difference between revisions of "GFeed-Service"
(→Data Pipes) |
(→Data Pipes) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
In the following example image we describe a capability scenario in which : | In the following example image we describe a capability scenario in which : | ||
| − | + | * C1,C2,C3,C4 are collectors (sources) | |
| − | + | * P1,P2 are controllers (destination) | |
| − | + | * C1,C2 support the transformation of data towards P2 | |
| − | + | * C3,C4 support the transformation of data towards P1 | |
Users can open close reported valves with their request parameters, thus (de)activating available pipes. | Users can open close reported valves with their request parameters, thus (de)activating available pipes. | ||
Revision as of 14:47, 2 February 2023
Aim of this service is to describe the implementation of gFeed-Service (for more information refer to GFeed).
Contents
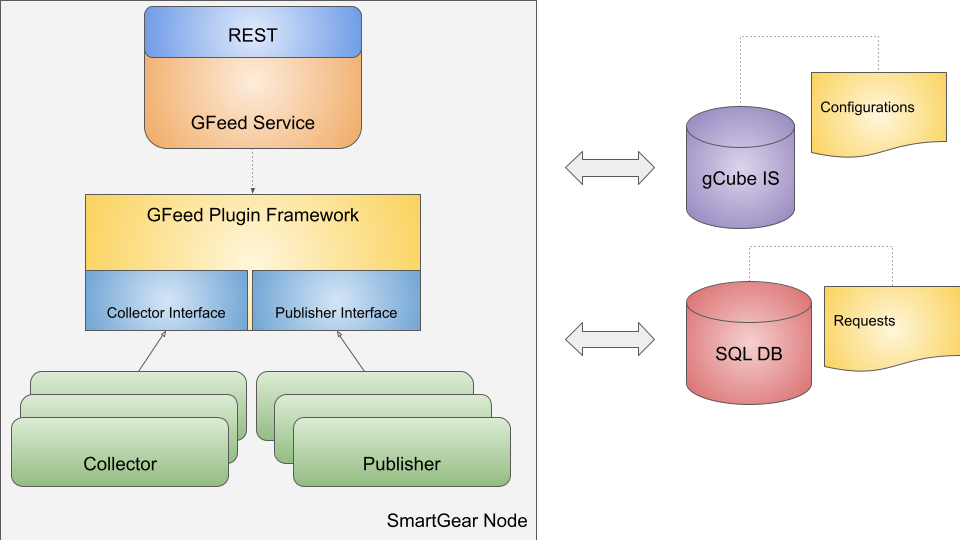
Architecture
GFeed service a gCube SmartGears web application with a REST-like interface, leveraging on gCube Framework capabilities for authentication, authorization and resource discovery through the gCube IS.
In order to maximize versatility and allow for extensions, it implements a plugin design patterns, delegating interaction with sources and destination to specific plugins. Such plugins implement specific Interfaces defined in a common plugin framework, that the service utilizes in order to discover available implementations and orchestrate requested execution.
Data Pipes
Gfeed aim is to enable batch information transfer between heterogeneous sources / destination. In order to do so, with each requests the users can specify which plugins to involve in the transfer, thus activating that particular source/destination in the process (Default is activate all).
For each request : 1. Data are harvested from activated sources by collector plugins 2. Collector plugins present harvested data to the service 3. For each activated destination ,the service asks collector plugins to transformation harvested data in proper destination data format (see Plugin Transformation Matrix) 4. Transformed data is passed to activated controllers for publication
We can summarize this behaviour by assuming all supported transformations as available data pipes from sources to destination. In such scenario, in each execution users activate this pipes as their were opening/closing related valves.
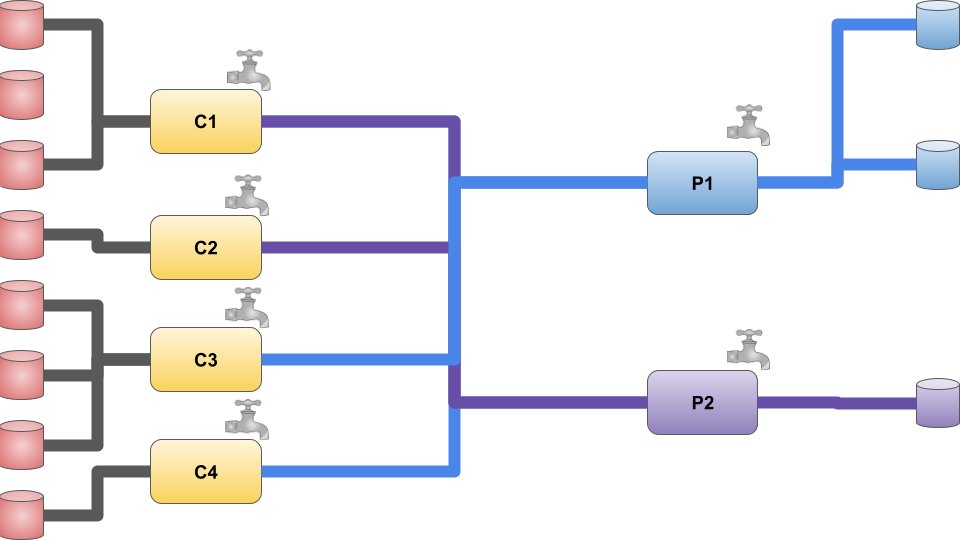
In the following example image we describe a capability scenario in which :
- C1,C2,C3,C4 are collectors (sources)
- P1,P2 are controllers (destination)
- C1,C2 support the transformation of data towards P2
- C3,C4 support the transformation of data towards P1
Users can open close reported valves with their request parameters, thus (de)activating available pipes.
Deployment
GFeed service utilizes the standard provisioning for smartgears service with plugins.
Plugins
Plugins are expected to be found in the service classpath. They are typically distributed as uber-jar and their deployment depends on the hosting container.
To see a complete list of available plugins implemetations please refer to gFeed-plugins-list
IS Requirements
IS Requirements are listed here.
HTTP Interface
Following is a list of methods exposed by gFeed HTTP interface. All methods require authentication so keep in mind that a gcube-token is expected. In this section <BASE_URL> stands for http(s)://<HOSTNODE>/gCat-Feeder/gcube/service/ where <HOSTNODE> should be determined by querying the gCube Information System.
Capabilities
Get available collectors
In order to get information on available collectors clients can perform a GET HTTP method on <BASE_URL>/capabilities/harvesters. The response is a JSON representation of available collectors.
Get available controllers
In order to get information on available controllers clients can perform a GET HTTP method on <BASE_URL>/capabilities/controllers. The response is a JSON representation of available controllers.
Executions
Submission
In order to submit an execution clients can perform a POST HTTP method on <BASE_URL>/execution. Following parameters are expected to be declared in the query string (multiple values can be specified):
- Parameter harvester
- expected value : to invoke collector ID
- default value ALL
- Parameter controller
- expected value : to invoke controller ID
- default value ALL
The resulting execution will be the combination of all requested harvester publishing their data to all requested controllers (only implemented transformation will be performed).
Available plugins ID can be retrieved by invoking related #Capabilities methods.
The resulting response is the ID of the submitted execution.
Examples
Following is a list of typical usages :
- Perform all available combinations : <BASE_URL>/execution
- Collect DataMiner Algorihtms information and push them in gCat service : <BASE_URL>/execution?harvester=DATAMINER_ALGORITHMS_COLLECTOR&controller=GCAT
Get submission history
In order to get the history of submitted executions clients can perform a GET HTTP method on <BASE_URL>/execution. The response is a JSON array of reports referring to submitted executions.
Get report
In order to get a report for a specific execution clients can perform a GET HTTP method on <BASE_URL>/execution/<EXECUTION_ID>, where <EXECUTUION_ID> is the id returned from submission method. Aim of this method is to monitor the outcome of a submitted execution (Asynch logic).
Please keep in mind that detailed reports are provided as a text file, accessible at reportUrl. The following is a report example :
{
"id": 4,
"collectors": [
"DATAMINER_ALGORITHMS_COLLECTOR"
],
"catalogues": [
"GCAT"
],
"callerEncryptedToken": ...,
"callerIdentity": ...,
"callerContext": ...,
"status": "SUCCESS",
"reportUrl": ...,
"startTime": ...,
"endTime": ...
}