Difference between revisions of "GCat Service"
Luca.frosini (Talk | contribs) (→HTTP Statuses) |
Luca.frosini (Talk | contribs) (→HTTP Statuses) |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
The most common error status a client can obtain are | The most common error status a client can obtain are | ||
| − | * '''''400 Bad Request''''' used to indicate a clients error [tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.1 tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.1]; | + | * '''''400 Bad Request''''' used to indicate a clients error [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.1 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.1]; |
* '''''401 Unauthorized''''' used to indicate that the client does not provided the gcube-token HTTP Header or the clinet has not enough right to perform such request [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-3.1 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-3.1]; | * '''''401 Unauthorized''''' used to indicate that the client does not provided the gcube-token HTTP Header or the clinet has not enough right to perform such request [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-3.1 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-3.1]; | ||
* '''''404 Not Found''''' used to indicate that the requested instance does not exists [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.4 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.4]; | * '''''404 Not Found''''' used to indicate that the requested instance does not exists [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.4 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.4]; | ||
| − | * '''''405 Method Not Allowed''''' the used HTTP method is not supported for the requested URL [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.5 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.5]. The response contains the ''Allow'' HTTP Header indicating the supported HTTP method for such URL [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.4.1 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.4.1]; | + | * '''''405 Method Not Allowed''''' the used HTTP method is not supported for the requested URL [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.5 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.5]. |
| + | The response contains the ''Allow'' HTTP Header indicating the supported HTTP method for such URL [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.4.1 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.4.1]; | ||
* '''''500 Internal Server Error''''' indicate a server failure. [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.1 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.1]. | * '''''500 Internal Server Error''''' indicate a server failure. [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.1 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.1]. | ||
Revision as of 18:18, 29 November 2018
The gCube Science Catalogue Service is a RESTful web service based on the principles defined in gCube Catalogue
Contents
Request
URL
The URL used to interact with the Science Catalogue Service is composed of two parts:
- Base Service URL (e.g. https:/catalogue.d4science.org/science-catalogue)
- Specific API (e.g. /organizations)
D4Science infrastructure uses cloud facilities allowing to replicate a service to achieve failover and load balancing.
Science Catalogue Service instances can be deployed and undeployed dynamically. For such a reason the Base Service URL MUST NOT be hard-cabled in the code because it can change over time.
To dynamically discover the Base Service URL please use the information system.
You need to discover gCore Resource having:
- class : DataCatalogue
- name : science-catalogue
HTTP Headers
gCube Authorization Token
Any request performed to Science Catalogue MUST contains the gCube Authorization Token.
This is done using the HTTP Header gcube-token
gcube-token: YOUR-TOKEN
The gcube-token HTTP header acts as the standard Authorization HTTP header. Plese note that Authorization HTTP header cannot be used in place of gcube-token HTTP header.
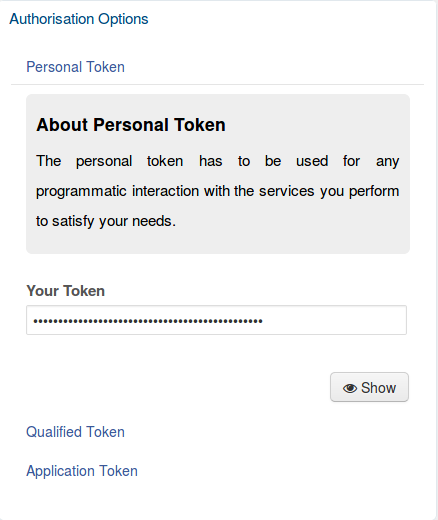
Retrieve your gCube Authorization Token
the gCube Authorization Token is a UUID bound to yourself and a given Infrastructure context. To retrieve it, you just need to go to a VRE for which you are interested and use the Authorisation Options portlet (see below)
Click on Show button and select the token.
Content Type
Any request must contain the indication of the interested content type.
For any operation returning a result, the client must specify the Accept HTTP Header.
Accept: application/json
For any operation sending content to the service, it is necessary to specify the Content-Type HTTP Header.
Content-Type: application/json
Actually, the service accepts and returns only JSON objects.
Except for a profile which can be also requested in XML.
HTTP Statuses
Any successful operation returns 200 OK status code except for create operation which return 201 Created.
The most common error status a client can obtain are
- 400 Bad Request used to indicate a clients error https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.1;
- 401 Unauthorized used to indicate that the client does not provided the gcube-token HTTP Header or the clinet has not enough right to perform such request https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-3.1;
- 404 Not Found used to indicate that the requested instance does not exists https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.4;
- 405 Method Not Allowed the used HTTP method is not supported for the requested URL https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.5.
The response contains the Allow HTTP Header indicating the supported HTTP method for such URL https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.4.1;
- 500 Internal Server Error indicate a server failure. https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.1.
A complete list of HTTP Status can be found here: https://httpstatuses.com/
You can report a 500 Internal Server Error the ticketing system. Please use this checklist before reporting an error:
- replicate the request
- the failure could be temporal due to network error, server issue so please retry the request after a certain amount of time
- indicate how to replicate the error
- indicate the time when the error occurred (this simplify the identification of the issue)
HTTP Methods
To be RESTful compliant Science Catalogue uses standard HTTP Methods to perform a listing of collections and CRUD (Create Read Update Delete) operations on instances.
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL | Success HTTP Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supported Methods | OPTIONS | /{COLLECTION} | 200 OK (Supported HTTP Methods in Allow HTTP Header) |
| List | GET | /{COLLECTION} | 200 OK |
| Create | POST | /{COLLECTION} | 201 Created |
| Supported Methods | OPTIONS | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 200 OK (Supported HTTP Methods in Allow HTTP Header) |
| Read | GET | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 200 OK |
| Update | PUT | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 200 OK |
| Patch | PATCH | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 200 OK |
| Delete | DELETE | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 200 OK |
| Purge | PURGE | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID} | 200 OK |
| Purge | DELETE | /{COLLECTION}/{INSTANCE_ID}?purge=true | 200 OK |
Where:
- {COLLECTION} is the plural name of the entity type
- {INSTANCE_ID} is an identification which enables to univocally identify the instance in the collection
You can find more information about this at https://restfulapi.net/http-methods/
PURGE Method is not a standard HTTP Method but is a widely used in service which requires this action (e.g. Varnish, Squid)
purge=true
Collections
Group Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /groups |
| Create | POST | /groups |
| Read | GET | /groups/{NAME} |
| Update | PUT | /groups/{NAME} |
| Patch | PATCH | /groups/{NAME} |
| Delete | DELETE | /groups/{NAME} |
| Purge | PURGE | /groups/{NAME} |
| Purge | DELETE | /groups/{NAME}?purge=true |
Item Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /items |
| Create | POST | /items |
| Read | GET | /items/{NAME} |
| Update | PUT | /items/{NAME} |
| Delete | DELETE | /items/{NAME} |
| Purge | PURGE | /items/{NAME} |
| Purge | DELETE | /items/{NAME}?purge=true |
Resource Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /items/{NAME}/resources |
| Create | POST | /items/{NAME}/resources |
| Read | GET | /items/{NAME}/resources/{ID} |
| Update | PUT | /items/{NAME}/resources/{ID} |
| Delete | DELETE | /items/{NAME}/resources/{ID} |
License Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /licenses |
Organization Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /organizations |
| Create | POST | /organizations |
| Read | GET | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Update | PUT | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Patch | PATCH | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Delete | DELETE | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Purge | PURGE | /organizations/{NAME} |
| Purge | DELETE | /organizations/{NAME}?purge=true |
User Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /users |
| Create | POST | /users |
| Read | GET | /users/{NAME} |
| Update | PUT | /users/{NAME} |
| Delete | DELETE | /users/{NAME} |
Profile Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /profiles |
| Read | GET | /profiles/{NAME} |
A profile is defined using XML. It is possible to get the original XML definition using 'Accept' HTTP Header.
Accept : application/xml
instead of
Accept : application/json
Namespace Collection
| Operation | HTTP Method | URL |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /namespaces |