Difference between revisions of "Resource Management Specification"
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) |
Manuele.simi (Talk | contribs) (→Key features) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
;Scalability | ;Scalability | ||
| − | : e-Infrastructures composed by thousands of nodes and software can be concurrently managed | + | :e-Infrastructures composed by thousands of nodes and software can be concurrently managed |
| + | |||
;Extensible Bridging over Virtual Platforms | ;Extensible Bridging over Virtual Platforms | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
;Cloud-orientation | ;Cloud-orientation | ||
| − | :Gateway to Cloud platforms with Java support | + | :Gateway to Cloud platforms with Java support, looking forward for the proposed [http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/tc_home.php?wg_abbrev=tosca Topology and Orchestration Specification for Cloud Applications] (or TOSCA) for short, standards specification |
== Design == | == Design == | ||
Revision as of 20:45, 26 February 2012
Overview
Resource Management focuses on the optimal exploitation of software and hardware resources. Software resources include a range of entities from packages ready to be deployed to already activated services, while hardware resources model platforms hosting a service suitable to be exploited by the e-infrastructure.
Resource Management covers the entire lifecycle of such resources through a set of services and libraries. This document outlines their design rationale, key features, and high-level architecture as well as the opportunities they collectively offer.
Key features
- Dynamic Deployment
- First-class features for deploying gCube software and external software packaged following the gCube policies, support for deployment of software hosted on recognized Maven repositories
- Optimal Resource Allocation
- Optimal selection and usage of resources during the deployment phase
- Node management and Monitoring
- Tools are provided for monitoring and managing nodes of the infrastructure. Local information are collected and published in the Information System as well as returned on demand. Web Service interfaces exposed by locally hosted services allow to remotely reconfigure the node upon the needs of the infrastructure.
- Scalability
- e-Infrastructures composed by thousands of nodes and software can be concurrently managed
- Extensible Bridging over Virtual Platforms
- A flexible model for transparently interfacing a potentially unlimited number of hosting environments.
- Maven Integration
- Any software available in a Maven repository can become part of the Data e-Infrastructure
- Coordination and Elastic Management
- ...
- Cloud-orientation
- Gateway to Cloud platforms with Java support, looking forward for the proposed Topology and Orchestration Specification for Cloud Applications (or TOSCA) for short, standards specification
Design
Philosophy
The Data e-Infrastructure requires dynamic allocation of services and nodes and a strong capability to adapt itself to changes occurring during its operation. Components of Resource Management subsystem address these requirements by providing a robust ground for the overall infrastructure lifetime.
Software has different externalizations at different level, ranging from a tarball of binaries to an activated instance hosted on a platform. Resource management has to be able to deal with such different forms and the designed architecture reflect this role.
Different components have different perceptions of the resources to manage. There are components operating at a logical level (VO and VRE) that only matter about how to optimize the VO/VRE delivered functionality by replicating/duplicating services when they see this need. These components do not obviously care of the physical form of the software and will never change if it will. Other components work at service level (the constituents of the VO/VRE) and know how to optimize their allocation. Finally, there exist components that operates at local level (node) and manage only local deployed software.
Other principles on which the design of the presented architecture is piled are:
- components must be generic with respect to the resource managed
- fault recovery is a crucial feature: nodes and services must be guaranteed to have in a consistent state under any condition
- external software has to be as transparently as possible managed in the same way of the gCube software
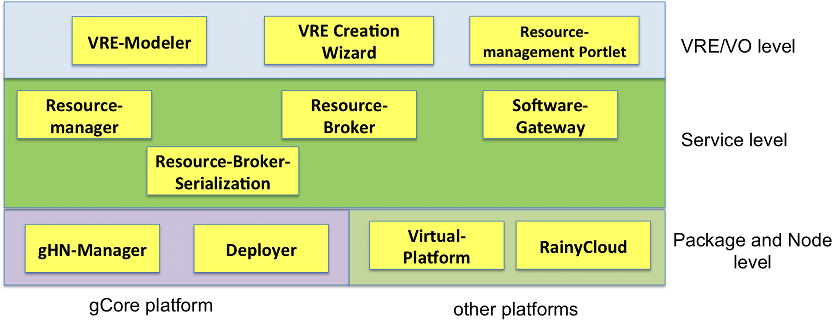
Architecture
- Resource-Manager
- Resource-Broker
- Resource-Broker-Serialization
- Software-Gateway
- VRE-Modeler
- gHN-Manager
- Deployer
- Virtual-Platform: a library with classes and interfaces to be extended/implemented to bridge and manage the lifecycle of software running on a different platform than gCore
- Virtual-Platform for Tomcat6: an implementation of the Virtual-Platform model to manage Web Applications on Apache Tomcat 6.x
- RainyCloud
Deployment
Usually, a subsystem consists of a number of number of components. This section describes the setting governing components deployment, e.g. the hardware components where software components are expected to be deployed. In particular, two deployment scenarios should be discussed, i.e. Large deployment and Small deployment if appropriate. If it not appropriate, one deployment diagram has to be produced.
Large deployment
A deployment diagram suggesting the deployment schema that maximizes scalability should be described here.
Small deployment
A deployment diagram suggesting the "minimal" deployment schema should be described here.
Use Cases
The subsystem has been conceived to support a number of use cases moreover it will be used to serve a number of scenarios. This area will collect these "success stories".