Difference between revisions of "Spatial Data Infrastructure Facilities"
m (→Specifications) |
(→Overview) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
<!-- CATEGORIES --> | <!-- CATEGORIES --> | ||
[[Category: gCube Spatial Data Infrastructure]] | [[Category: gCube Spatial Data Infrastructure]] | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | gCube | + | gCube Spatial Data Infrastructure facilities realize a rich array of services for managing spatial datasets and associated metadata. |
| + | |||
| + | Such facilities are implemented by relying on state-of-the-art technologies and standards, e.g. [http://www.opengeospatial.org/standards OGC W*S], [https://www.geonetwork-opensource.org/ GeoNetwork], [https://www.unidata.ucar.edu/software/thredds/current/tds/ THREDDS Data Server]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It offers standard-based services for | ||
| + | * [[Spatial Data Discovery and Access | data discovery]] (a catalogue), | ||
| + | * [[Spatial Data Storage | storage and access]] (a federation of repositories), | ||
| + | * [[Spatial Data Processing | processing]] (an extensible analytic platform), | ||
| + | * [[Spatial Data Discovery and Access | visualisation]] (a map container). | ||
| + | The catalogue service enables the discovery of geospatial data residing in dedicated repositories by relying on a CSW-based service (namely GeoNetwork) and its indexing facilities. | ||
| + | For data storage and access, gCube offers a federation of repositories based on GeoServer and THREDDS technologies. | ||
| + | In essence, the infrastructure hosts a number of repositories and a [[GIS Publisher Service]] that enables a seamless publication of spatial data while guaranteeing load balancing, failure management and automatic metadata generation. | ||
| + | It relies on an open set of back-end technologies for the actual storage and retrieval of the data. | ||
| + | Because of this, the [[GIS Publisher Service]] is designed with a plug-in-oriented approach where each plug-in interfaces with a given back-end technology. | ||
| + | To enlarge the array of supported technologies it is sufficient to develop a dedicated plug-in. | ||
| + | Metadata on available data are published by the catalogue. | ||
| + | For data visualisation, the infrastructure offers [[Geo Explorer]] and [[GIS Viewer]], two components dedicated to support the browsing and visualisation of geospatial data. | ||
| + | In particular, the [[Geo Explorer]] is a web application that allows users to navigate, organize, search and discover layers from the catalogue via the CSW protocol. The GIS Viewer is a web application that allows users to interactively explore, manipulate and analyse geospatial data. | ||
This page collects the specifications related to the three key-areas of the facilities. | This page collects the specifications related to the three key-areas of the facilities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:GCube SDI Overall.jpg|center|1000px]] | ||
== Specifications == | == Specifications == | ||
| − | [[Spatial Data Storage]] | + | [[Spatial Data Storage and Publishing]] |
[[Spatial Data Processing]] | [[Spatial Data Processing]] | ||
[[Spatial Data Discovery and Access]] | [[Spatial Data Discovery and Access]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:39, 13 July 2018
Overview
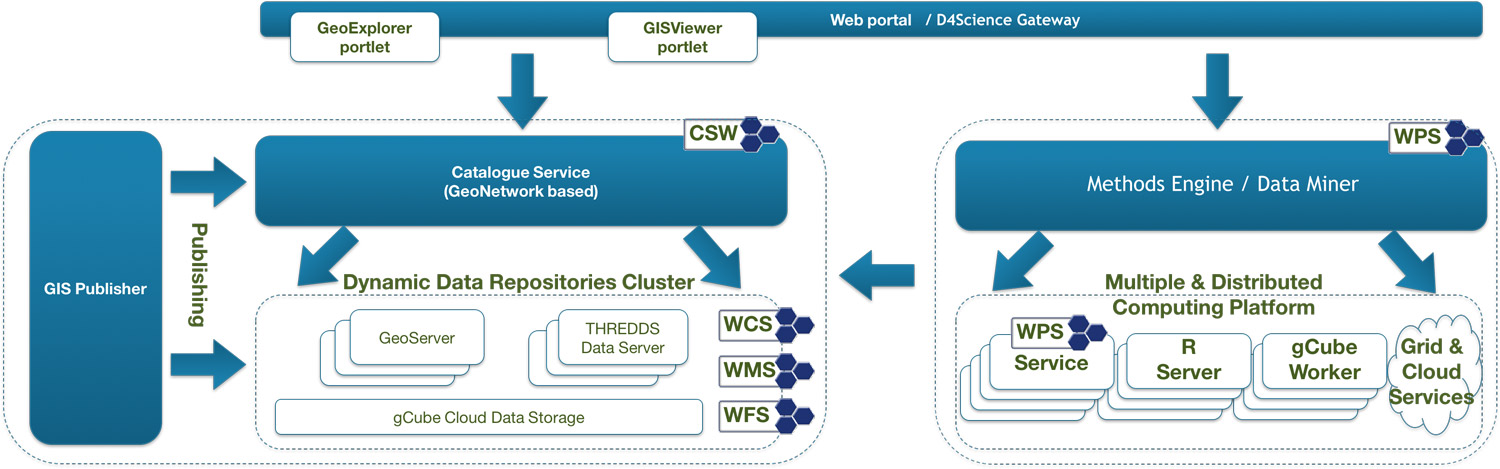
gCube Spatial Data Infrastructure facilities realize a rich array of services for managing spatial datasets and associated metadata.
Such facilities are implemented by relying on state-of-the-art technologies and standards, e.g. OGC W*S, GeoNetwork, THREDDS Data Server.
It offers standard-based services for
- data discovery (a catalogue),
- storage and access (a federation of repositories),
- processing (an extensible analytic platform),
- visualisation (a map container).
The catalogue service enables the discovery of geospatial data residing in dedicated repositories by relying on a CSW-based service (namely GeoNetwork) and its indexing facilities. For data storage and access, gCube offers a federation of repositories based on GeoServer and THREDDS technologies. In essence, the infrastructure hosts a number of repositories and a GIS Publisher Service that enables a seamless publication of spatial data while guaranteeing load balancing, failure management and automatic metadata generation. It relies on an open set of back-end technologies for the actual storage and retrieval of the data. Because of this, the GIS Publisher Service is designed with a plug-in-oriented approach where each plug-in interfaces with a given back-end technology. To enlarge the array of supported technologies it is sufficient to develop a dedicated plug-in. Metadata on available data are published by the catalogue. For data visualisation, the infrastructure offers Geo Explorer and GIS Viewer, two components dedicated to support the browsing and visualisation of geospatial data. In particular, the Geo Explorer is a web application that allows users to navigate, organize, search and discover layers from the catalogue via the CSW protocol. The GIS Viewer is a web application that allows users to interactively explore, manipulate and analyse geospatial data.
This page collects the specifications related to the three key-areas of the facilities.