Difference between revisions of "GCube Security Model"
(→Model) |
(→Model) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==Authorization == | ==Authorization == | ||
===Model=== | ===Model=== | ||
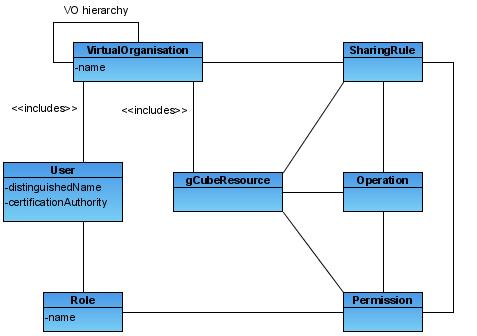
| − | Authorization rights in DILIGENT are modeled basing on the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Role-Based_Access_Control RBAC] model. This means that each user need to held a valid role to operate in the DILIGENT infrastructure. | + | Authorization rights in DILIGENT are modeled basing on the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Role-Based_Access_Control RBAC] model. This means that each user need to held a valid role to operate in the DILIGENT infrastructure. Following diagram shows the DILIGENT VO model. |
[[Image:VO_Model.jpg]] | [[Image:VO_Model.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 14:39, 22 May 2007
This page describes the security model adopted in the DILIGENT Security infrastructure
Contents
Authentication
Model
The DILIGENT Security model uses Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) mechanisms to authenticate identities acting in the infrastructure.
Each authenticated invocation must be performed using valid credentials issued by a trusted Certification Authority (CA).
To speed-up performances of some Running Instances (RI) unauthenticated invocatons are also allowed, even if not included in the design of DILIGENT security. These invocations can be performed without any credentials, neither authentication nor authorization are enforced in these cases.
Mechanism
The mechanism used in DILIGENT to authenticate RI invocatons is the WS-SecureConversation one. The Java WS-Core container provides a built-in implementation of this standard called GSI-SecureConversation.
This choice is driven by the need to delegate caller credentials to invoked RI. The HTTPS mechanism (also available in the Java-WS-Core) cannot interoperate with the GSI-SecureConversation one, thus preventing the exploiting of both mechanisms in the DILIGENT infrastructure. For this reason the HTTPS mechanism has been discarded.
Authorization
Model
Authorization rights in DILIGENT are modeled basing on the RBAC model. This means that each user need to held a valid role to operate in the DILIGENT infrastructure. Following diagram shows the DILIGENT VO model.
Mechanism
A VOMS server maintains the Digital Library (DL) hierarchy as a VOMS groups hierarchy. Roles are defined globally in DILIGENT and are granted to users in a DL (thus in a VOMS group). When a user logs in the portal fresh proxy credentials are created for it. These credentials contains roles held by the user during session.
The DL context
Authenticated invocations to DILIGENT RI are performed in the context of a DL. The context is identified from the proxy certificate attached to the request. The user is supposing to operate in the DL corresponding to the VOMS group that contains at least one role in the proxy credentials.
As a consequence of this choice in DILIGENT all roles included in a proxy certificate must be bound to the same group. This allows to univocally identify the VOMS group where the user is operating, thus the corresponding DL. This of course does not work for unauthenticated invocations.
![]() As a VOMS design choice, all groups the user is member of are always included in the proxy during creation. Role/s to be included need to be explicitly required by the user.
As a VOMS design choice, all groups the user is member of are always included in the proxy during creation. Role/s to be included need to be explicitly required by the user.
Identities for DILIGENT services
DILIGENT RIs need certificates in order to:
- Autonomously operates in the infrastructure
- Perform further service calls (while serving a request) without the need to impersonate the caller
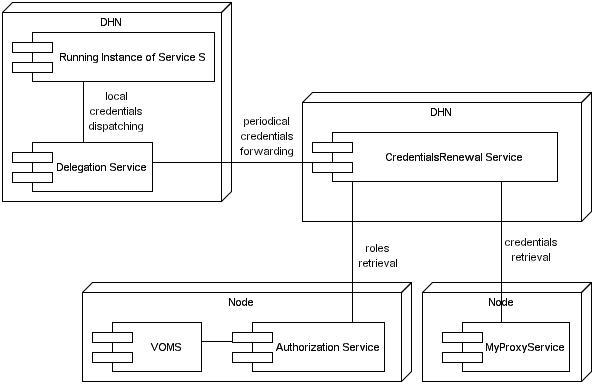
The Delegation and Credentials Renewal services developed in DILIGENT allows RI to periodically receive fresh credentials to perform invocations.
The CredentialsRenewal service allows users to set renewal tasks. Each task contains:
- The MyProxy account where to retrieve credentials
- The Delegation service where to forward them
- The Name of the service where credentials have to be dispatched
- A set of VOMS roles to be added to credentials
Each task periodically retrieve credentials from a MyProxy repository and forward them to the Delegation service co-hosted with the service. The Delegation act as a local dispatcher, notifying the service when fresh credentials are received.
Alongside functonalities provided by these services, the delegation mechanism built-in into the GSISecureConversation protocol is also available. It allows a RI to impersonate the caller.
Two scenarios can be foreseen for DILIGENT RI credentials:
Identity of RI acting in a Single DL
These RIs are able to act in a single DL, thus they need only a single copy of credentials containing roles for that DL.
These RIs can also support unauthenticated incoming requests, as they always operate in the infrastructure using the same identity.
Identity of RI acting in mutiple DLs
These RIs needs to act in mulltiple DLs, thus they need different identities ( one for each DL where they operate). Moreover they need to select right credentials to use for RI invocations. This choice is driven by the DL where the caller is operating. This DL can be identified from the caller certificate (see The DL context section)
For this reason these RIs cannot support unauthenticated incoming requests, as they need to know in which DL the caller is operating.