Difference between revisions of "The GCube Information Organisation Services"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The ''Information Organisation'' services are dedicated to the management of content in gCube, including storage, access, description and annotation. | The ''Information Organisation'' services are dedicated to the management of content in gCube, including storage, access, description and annotation. | ||
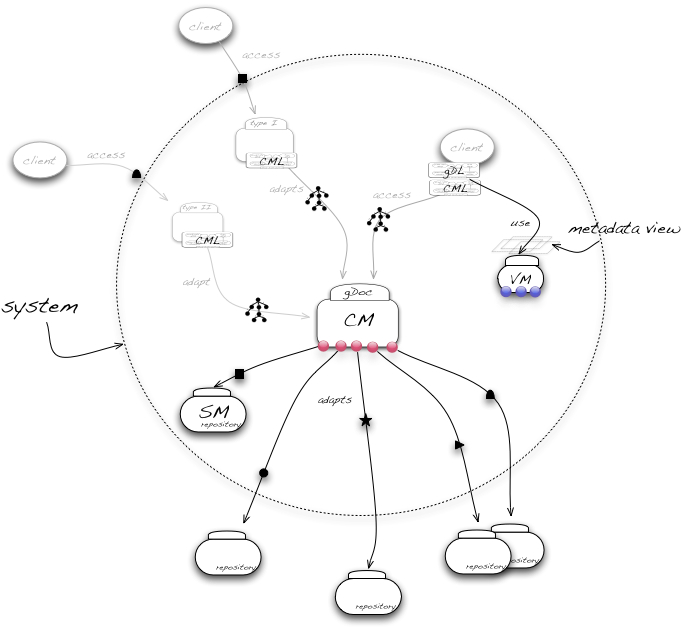
| − | The services form a subsystem with an hourglass-shaped architecture. Central to the hourglass is the [[Content Manager (NEW)|Content Manager]] (CM), a service that provides uniform access to content served by a variety of back- | + | The services form a subsystem with an hourglass-shaped architecture. Central to the hourglass is the [[Content Manager (NEW)|Content Manager]] (CM), a service that provides uniform access to content served by a variety of back-ends, both inside and outside the system. The Content Manager exposes CRUD operations over a content model of edge-labelled trees, and it relies on plugins to dynamically adapt to an arbitrary number of back-ends. |
Back-ends may include storage services as well as access services to content stored further afield. Part of the subsystem is the [[Storage Manager (NEW)|Storage Manager]] (SM), a storage service that organises content in a web of binary relationships between Information Objects. | Back-ends may include storage services as well as access services to content stored further afield. Part of the subsystem is the [[Storage Manager (NEW)|Storage Manager]] (SM), a storage service that organises content in a web of binary relationships between Information Objects. | ||
Revision as of 22:46, 26 August 2010
The Information Organisation services are dedicated to the management of content in gCube, including storage, access, description and annotation.
The services form a subsystem with an hourglass-shaped architecture. Central to the hourglass is the Content Manager (CM), a service that provides uniform access to content served by a variety of back-ends, both inside and outside the system. The Content Manager exposes CRUD operations over a content model of edge-labelled trees, and it relies on plugins to dynamically adapt to an arbitrary number of back-ends.
Back-ends may include storage services as well as access services to content stored further afield. Part of the subsystem is the Storage Manager (SM), a storage service that organises content in a web of binary relationships between Information Objects.
The clients of the Content Manager may also be internal or external to gCube. Clients included in the subsystem are the Metadata Manager (MM) and the Annotation Manager (AM), two services that describe and annotate content, respectively.
All the services in the subsystem align with the design patterns of an abstract architecture, the Open Content Management Architecture.